Oxygen biogeochemistry exerts a strong influence on cobalt cycling
This is an important result of the US GEOTRACES East Pacific Zonal Transect (EPZT) cruise (GP16) discussed by Hawco and his co-workers (2016, see reference below). The distribution of dissolved cobalt and labile cobalt along this section is closely tied to the oxygen minimum zone. This work also shows that (1) elevated concentrations of labile cobalt are generated by input from coastal sources and reduced scavenging at low oxygen; (2) atmospheric deposition and hydrothermal vents along the East Pacific Rise are contrastingly minor sources of cobalt; (3) high cobalt waters are further upwelled and advected offshore and; (4) phytoplankton export returns cobalt to low-oxygen water masses underneath. These processes result in covariation of dissolved cobalt with oxygen and phosphates, schematically represented in the Figure below.
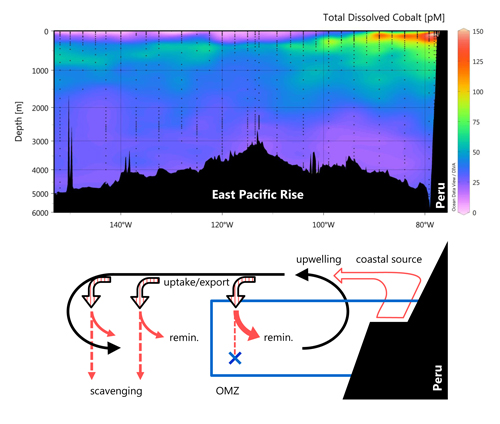
Figure: In the South Pacific Ocean, high levels of cobalt are harbored in waters that are devoid of dissolved oxygen (upper panel, warm colors). This plume of cobalt stems from the Peru coast and is enhanced by degradation of cobalt-bearing phytoplankton in these waters, and by the absence of removal processes (scavenging) when oxygen is low (lower panel).
Reference:
Hawco, N. J., Ohnemus, D. C., Resing, J. A., Twining, B. S., & Saito, M. A. (2016). A dissolved cobalt plume in the oxygen minimum zone of the eastern tropical South Pacific. Biogeosciences, 13(20), 5697–5717. DOI: 10.5194/bg-13-5697-2016
