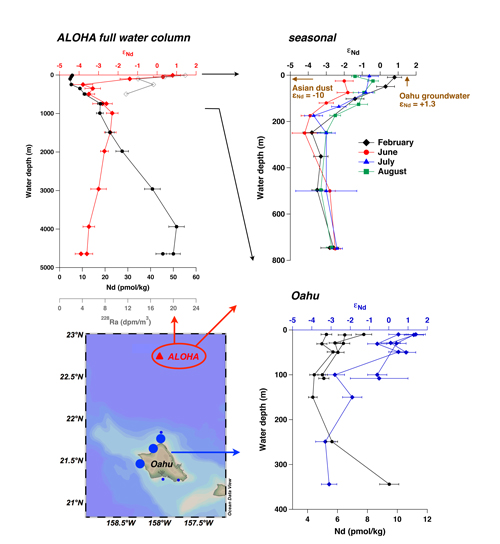
Lithogenic influence from the Hawaiian Islands detectable up to Station ALOHA surface waters
By coupling neodymium (Nd) and radium (Ra) isotopes and Rare Earth Element (REE) signals, Henning Fröllje and co-workers (2016, see reference below) show that the coastal Hawaiian waters are affected by a prominent lithogenic influence from the Hawaiian Islands. Rare earth patterns, radiogenic εNd signatures and high 228Ra levels are clearly tracing this influence. Moreover, it is perceptible as far as ALOHA station (100 km north). This influence at ALOHA is most pronounced in February, when precipitation on the islands is highest and dust input from Asia is low. In summer, however, Nd isotopes are shifted towards the Asian dust endmember (εNd = -10), indicating seasonal dust influence overlying the Hawaiian background signal.
A close study of the rare earth distribution and speciation confirm that these elements are truly dissolved in seawater and that they are following water mass advection and mixing in the intermediate and deep central North Pacific Ocean.
Reference:
Fröllje, H., Pahnke, K., Schnetger, B., Brumsack, H.-J., Dulai, H., & Fitzsimmons, J. N. (2016). Hawaiian imprint on dissolved Nd and Ra isotopes and rare earth elements in the central North Pacific: Local survey and seasonal variability. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 189, 110–131. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2016.06.001
