Gadolimium, a Rare Earth Element becoming a human contaminant and tracer of wastewater discharge in the ocean
Gadolinium (Gd) is increasingly used in contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging. It is therefore released in the wastes of hospitals and research centres.
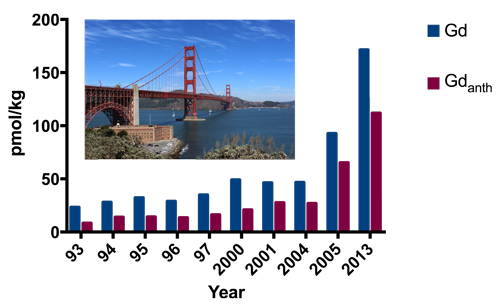
As a consequence, Hatje and collaborators (2016, see reference below) showed that anthropogenic Gd concentrations in San Francisco Bay increased by an order of magnitude over the past 2 decades, even reaching the northeast Pacific coastal waters. Beyond the fact that such input might be used as tracers of wastewater discharges and hydrological processes, such impressive environmental change suggests that more effective treatment technologies may be necessary to minimise future contamination by chemical elements specially rare earth elements (REE, such as Gd) that are critical for the development of new technologies.
Reference:
Hatje, V., Bruland, K. W., & Flegal, A. R. (2016). Increases in Anthropogenic Gadolinium Anomalies and Rare Earth Element Concentrations in San Francisco Bay over a 20 Year Record. Environmental Science & Technology, 50(8), 4159–4168. doi:10.1021/acs.est.5b04322
