52 years of Benthic Nepheloid Layer data!
A data base of 2412 profiles collected using the Lamont Thorndike nephelometer from 1964 to 1984 is used to globally map turbid nepheloid layers by Gardner and co-workers (2018, see reference below). The authors compare maps from that period with maps based on data from 6392 profiles measured using transmissometers from 1979 to 2016 (see GEOTRACES science highlight about this paper ). Beyond this comparison, the final goal is to gain insight about the factors creating/sustaining Benthic Nepheloid Layers (BNLs). Eleven maps, including mean surface Kinetic Energy (KE), are discussed here. The similarity between general locations of high and low particle concentration BNLs during the two time periods indicates that the driving forces of erosion and resuspension of bottom sediments are spatially persistent during recent decadal time spans, though in areas of strong BNLs, intensity is highly episodic. This work confirms that topography, well-developed current systems, and surface KE and EKE play a role in generating and maintaining BNLs.
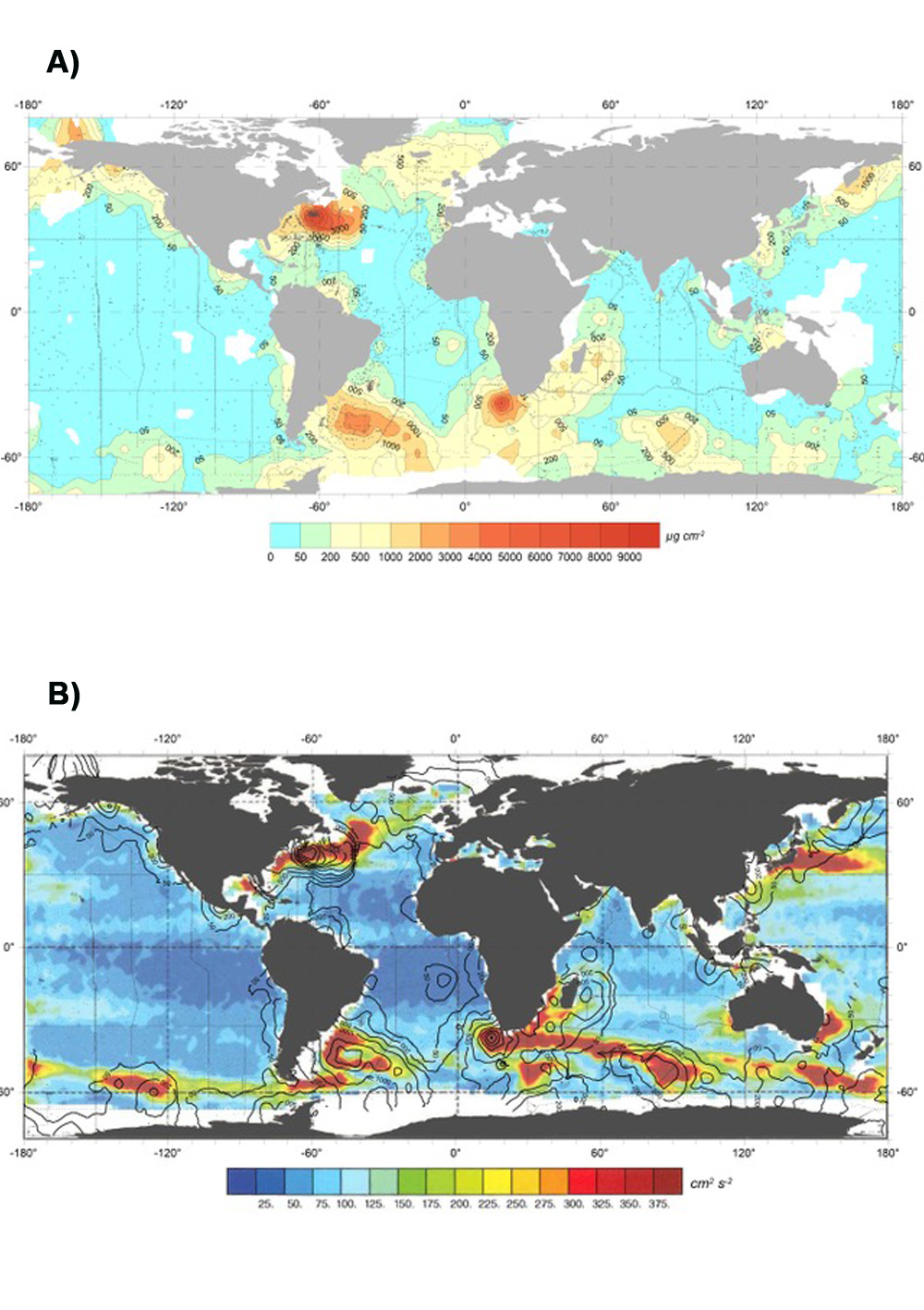 Figure: A) Excess particulate matter in “strong” nepheloid layers (> 20 μg l-1) based on transmissometer (cp) and nephelometer (E/ED) profiles. B) Mean Kinetic Energy per unit mass, cm2 s-2, in surface waters, derived from four years of satellite altimetric data and using the geostrophic relationship (adapted from Wunsch, 2015). Black contours superimposed are Excess particulate matter in “strong” nepheloid layers (> 20 μg l-1 from Figure A). Click here to view the figure larger.
Figure: A) Excess particulate matter in “strong” nepheloid layers (> 20 μg l-1) based on transmissometer (cp) and nephelometer (E/ED) profiles. B) Mean Kinetic Energy per unit mass, cm2 s-2, in surface waters, derived from four years of satellite altimetric data and using the geostrophic relationship (adapted from Wunsch, 2015). Black contours superimposed are Excess particulate matter in “strong” nepheloid layers (> 20 μg l-1 from Figure A). Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Gardner, W. D., Richardson, M. J., Mishonov, A. V., & Biscaye, P. E. (2018). Global comparison of benthic nepheloid layers based on 52 years of nephelometer and transmissometer measurements. Progress in Oceanography, 168(May), 100–111. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2018.09.008
