Widespread nutrient co-limitation discovered on GEOTRACES cruise
Browning and co-workers (2017, see reference below) find that multiple nutrients must be supplied to stimulate phytoplankton growth on the southeast Atlantic GEOTRACES GA08 cruise. The paper has been published in Nature.
Experiments to date have suggested that across most of the ocean surface marine phytoplankton are limited by either nitrogen or iron. But simultaneously low concentrations of these and other nutrients have been measured over large extents of the open ocean, raising the question: are phytoplankton in these waters only limited by one nutrient?
Browning and co-workers tested this by conducting experiments throughout the SE Atlantic GEOTRACES GA08 cruise, where seawater samples were amended with nitrogen, iron, and cobalt—alone and in all possible combinations. They found that adding both nitrogen and iron in combination was needed to stimulate any significant phytoplankton growth over 1000s of kilometres of ocean. Furthermore, addition of cobalt in combination with nitrogen and iron further enhanced phytoplankton growth in a number of experiments.
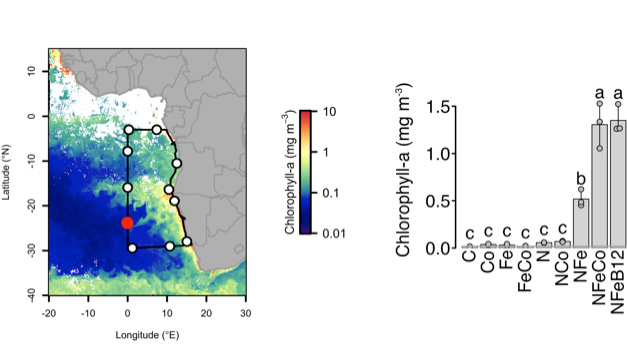 Figure: Experiments were conducted throughout the SE Atlantic GEOTRACES cruise transect (lines and dots on the map) and demonstrated that nitrogen and iron had to be added to significantly stimulate phytoplankton growth. Supplementary addition of cobalt (or cobalt-containing vitamin B12) stimulated significant additional growth. Experimental responses illustrated in the right panel are from the site indicated by the red point on the map. Click here to view the figure larger.
Figure: Experiments were conducted throughout the SE Atlantic GEOTRACES cruise transect (lines and dots on the map) and demonstrated that nitrogen and iron had to be added to significantly stimulate phytoplankton growth. Supplementary addition of cobalt (or cobalt-containing vitamin B12) stimulated significant additional growth. Experimental responses illustrated in the right panel are from the site indicated by the red point on the map. Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Browning, T.J., Achterberg, E.P., Rapp, I., Engel, A., Bertrand, E.M., Tagliabue, A. and Moore, C.M., 2017. Nutrient co-limitation at the boundary of an oceanic gyre. Nature. 551, 242–246 doi:10.1038/nature24063.
