What is generating the benthic nepheloid layers?
How ubiquitous, variable or persistent are nepheloid layers? What is the main process generating these “clouds at the bottom of the sea”? Gardner and co-workers (2017, see reference below) explore these two critical questions, with a focus on the western North Atlantic for which numerous time series and survey data exist. They piece together a detailed review of the mechanisms and provide important new insights into the creation, persistence, and decay of nepheloid layers, a major issue for the geochemistry of particle-reactive elements. Their main results are: Deep western boundary currents are too weak to create benthic storms and therefore to generate intense nepheloid layers; benthic storms are created primarily by deep cyclones beneath Gulf Stream meanders; benthic storms erode the seafloor and maintain the benthic nepheloid layer; and finally, benthic nepheloid layers are weak to non-existent in areas of low eddy kinetic energy.
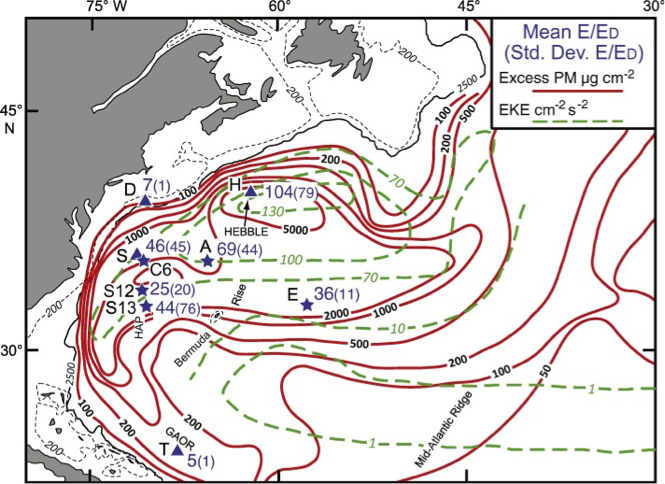
Figure 1: Contours of integrated benthic particle load (red lines, in μg cm− 2) and abyssal eddy kinetic energy (EKE, dashed green lines, in cm2 s− 2). Numbers by stars and triangles are related to the mean time-series particle concentration and standard deviation of particle concentration (in parentheses). Click here to view the figure larger.
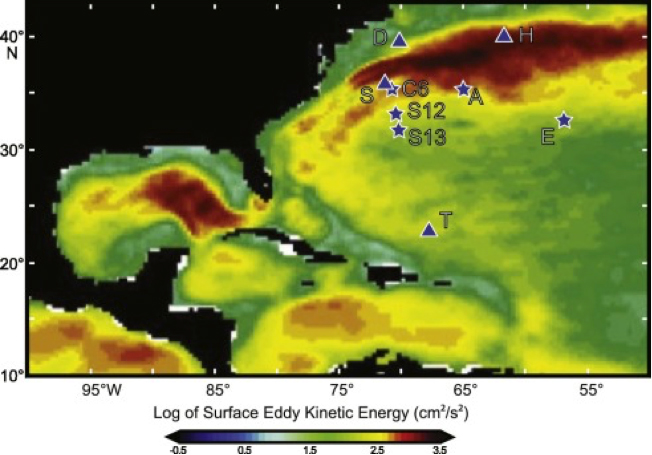
Figure 2: Map of surface EKE based on satellite observations during 2002–2006 (Dixon et al., 2011). Time-series stations are indicated. Click here to view the figure larger.
References:
Gardner, W. D., Tucholke, B. E., Richardson, M. J., & Biscaye, P. E. (2017). Benthic storms, nepheloid layers, and linkage with upper ocean dynamics in the western North Atlantic. Marine Geology. DOI:10.1016/j.margeo.2016.12.012 Open Access
K.W. Dixon, T.L. Delworth, A.J. Rosati, W. Anderson, A. Adcroft, V. Balaji, R. Benson, S.M. Griffies, H.-C. Lee, R.C. Pacanowski, G.A. Vecchi, A.T. Wittenberg, F. Zeng, R. Zhang Ocean circulation features of the GFDL CM2.6 & CM2.5 high-resolution global coupled climate models. WCRP Open Science Conference, October 2011, Denver, Colorado (2011)
