What controls the copper isotopic composition in oceanic waters?
Takano and co-workers (2014, see reference below) strongly suggest that the isotopic composition of dissolved copper (δ65Cu) in surface seawater is mainly controlled by supply from rivers, the atmosphere and deep seawater. This is the conclusion of a study involving six vertical profiles of copper (Cu) concentration and isotopes measured in the Indian (1) and North Pacific Oceans (5). The finding contradicts previous interpretations suggesting a strong role of the biological activity in δ65Cu fractionation.
At depth, δ65Cu values are becoming heavier with the age of deep seawater, likely due to preferential scavenging of the light isotope (63Cu). The authors built a box-model to quantify the oceanic budgets of both Cu concentrations and δ65Cu. Imbalance in this model suggests that Cu fluxes from continental shelf sediment might affect Cu distribution in the open ocean.
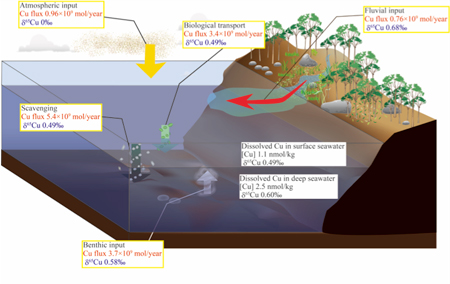
Figure: A box-model of Cu in the ocean based on both Cu concentration and isotopic composition. Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Takano, S., Tanimizu, M., Hirata, T., & Sohrin, Y. (2014). Isotopic constraints on biogeochemical cycling of copper in the ocean. Nature Communications, 5, 5663. doi:10.1038/ncomms6663 Click here to view the paper.
