Variable dissolution rates and fates of lithogenic tracers at the air-sea interface
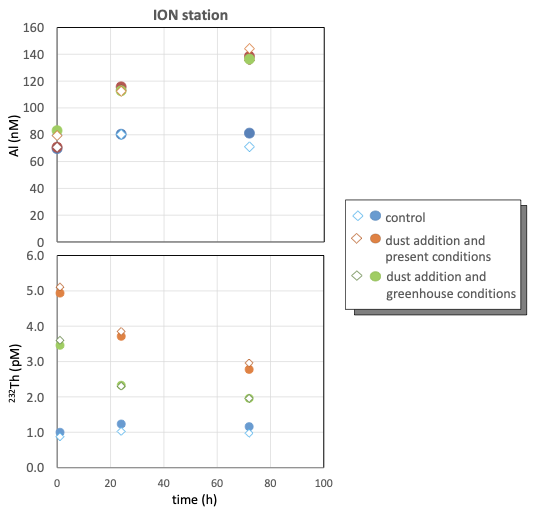
Lithogenic elements such as aluminum (Al), iron (Fe), rare earth elements (REEs), thorium (232Th and 230Th, given as Th) and protactinium (Pa) are often assumed to be insoluble. Roy-Barman and co-authors (2021, see reference below) established the dissolution rates from Saharan dust reaching Mediterranean seawater. Their experiments included dust seeding under present and future climate conditions (+3 ∘C and −0.3 pH). The maximum dissolution was low for all seeding experiments: less than 0.3 % for Fe, 1 % for 232Th and Al, about 2 %–5 % for REEs and less than 6 % for Pa. Different behaviours were observed: dissolved Al increased until the end of the experiments, Fe did not dissolve significantly, and Th and light REEs were scavenged back on particles after a fast-initial release. The constant 230Th/232Th ratio during the scavenging phase suggests that there is little or no further dissolution after the initial Th release. Comparison of present and future conditions indicates that changes in temperature and/or pH influence the release of Th and REEs in seawater, leading to lower Th release and a higher light REE release under increased greenhouse conditions.
Reference:
Roy-Barman, M., Foliot, L., Douville, E., Leblond, N., Gazeau, F., Bressac, M., Wagener, T., Ridame, C., Desboeufs, K., and Guieu, C. (2021) Contrasted release of insoluble elements (Fe, Al, rare earth elements, Th, Pa) after dust deposition in seawater: a tank experiment approach, Biogeosciences, 18, 2663–2678, Access the paper: https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-18-2663-2021
