Uranium-238 data and physical transports off the Peruvian coast are questioning the thorium-uranium export model
Thorium-234 (234Th) is a widely used tracer for element export fluxes from the ocean surface. However, its application requires a relatively quiet ocean dynamic and constant distribution of the conservative uranium-238 (238U): both conditions are not optimal off the Peruvian coast, to say the least. Using vessel-mount acoustic current Doppler profiler instrument, satellite wind speed and in situ microstructure measurements, Xie and co-workers (2020, see reference below) determined insignificant advective and diffusive 234Th fluxes at 25 stations from 11 to 16ºS in the Peruvian oxygen minimum zone. They also revealed that in this area, 238U is not anymore correlated to salinity, in other words conservative. Despite these obstacles, they provide 234Th- export fluxes at 100 m ranging from 850 to 3400 dmp.m-2.d-1, although warn the community of the limits of the Th-U model in such coastal area!
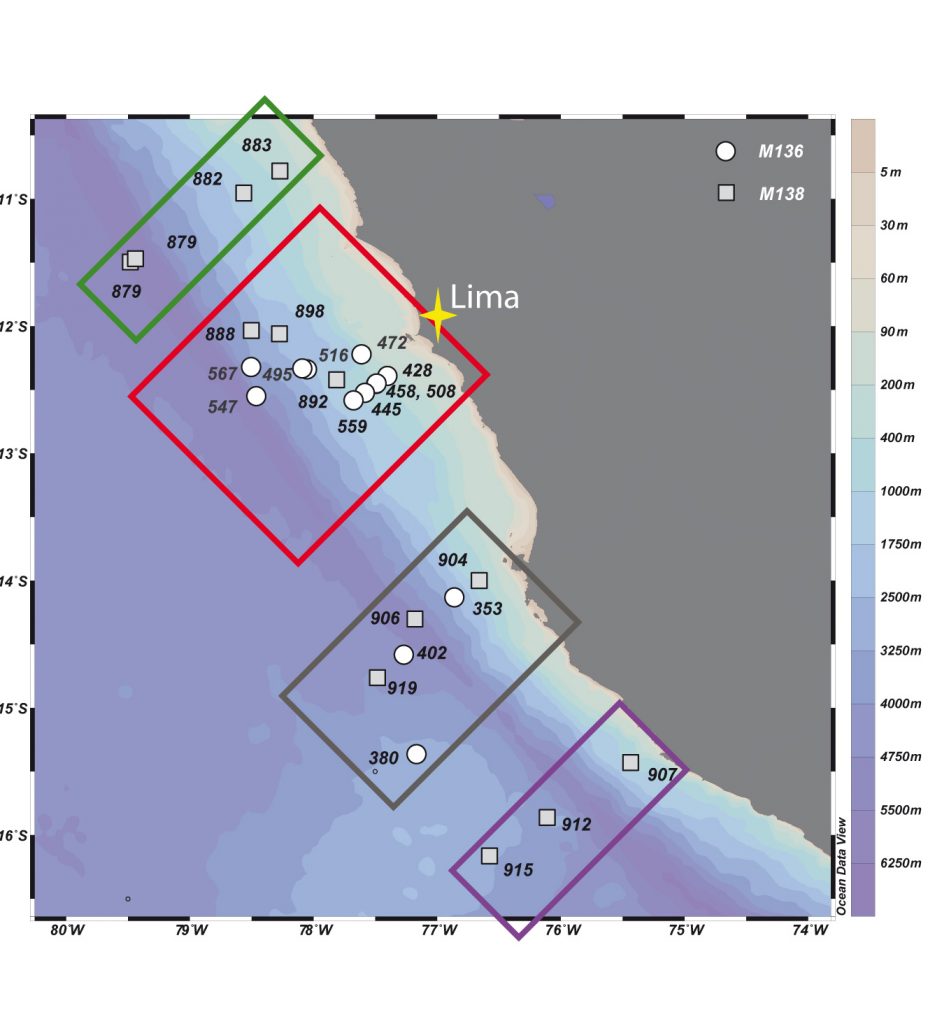
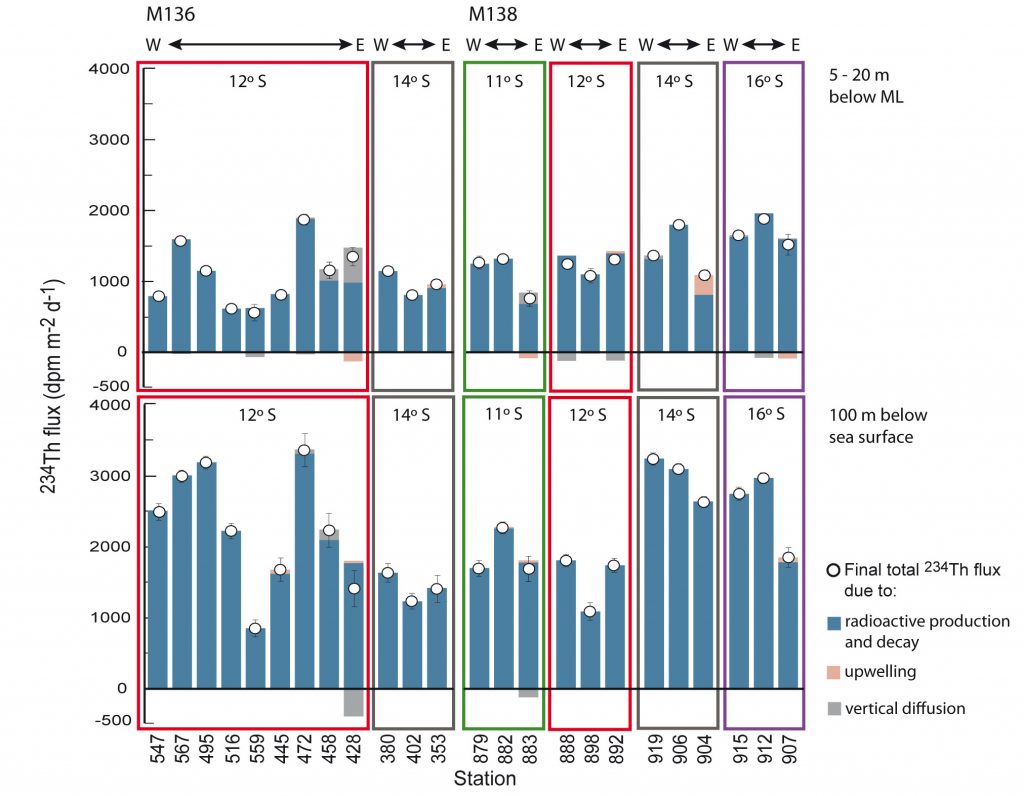
Map on the top panel shows locations of stations from M136 (circles) and M138 (white) off the coast of Peru. Color boxes schematically divide the four shelf-offshore transects. The bar chart on bottom panel shows the total 234Th flux (white circles) as a consequence of radioactive production and decay (blue), upwelling (pink) and vertical diffusion (grey) for the depths at 5-20 m below the ML (top) and 100 m below sea surface (bottom).
Reference:
Xie, R. C., Le Moigne, F. A. C., Rapp, I., Lüdke, J., Gasser, B., Dengler, M., Liebetrau, V., Achterberg, E. P. (2020). Effects of 238U variability and physical transport on water column 234Th downward fluxes in the coastal upwelling system off Peru. Biogeosciences, 17(19), 4919–4936. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-17-4919-2020
