Using the three thorium isotope toolbox to probe the particle dynamic within an East Pacific Rise hydrothermal plume
The insoluble radiogenic isotopes of thorium (Th) are produced at a known rate in the water column via the decay of soluble uranium (234Th, 230Th) and radium (228Th) isotopes. These three isotopes are radioactive and their half-lives vary from days (234Th) to years (228Th) to tens of thousands of years (230Th). Combining their known production and decay rates with their insolubility makes them excellent tools to study the particle dynamics on a wide range of timescales.
This toolbox was successfully used by Pavia and co-workers (2019, see reference below) to study particle-dissolved exchange within the hydrothermal plume detected during the GEOTRACES GP16 cruise in the southeast Pacific Ocean. The goal of these authors was to unravel how hydrothermal activity affects the different steps characterizing the scavenging processes, i.e. adsorption and desorption onto particles, particle aggregation, sinking, and eventual sedimentation.
Their main conclusions are that: 1) particle aggregation was occurring much more rapidly in the plume, 2) hydrothermal scavenging is partially irreversible, 3) off-axis hydrothermal Th scavenging rate of 0.15yr−1, value deduced from a modelling and 4) 230Th is surprisingly more depleted than the two other isotopes. This likely reflects progressive scavenging in this region of intense hydrothermal activity and underlines the complexity of interpreting the GP16 hydrothermal plume as being solely a local phenomenon.
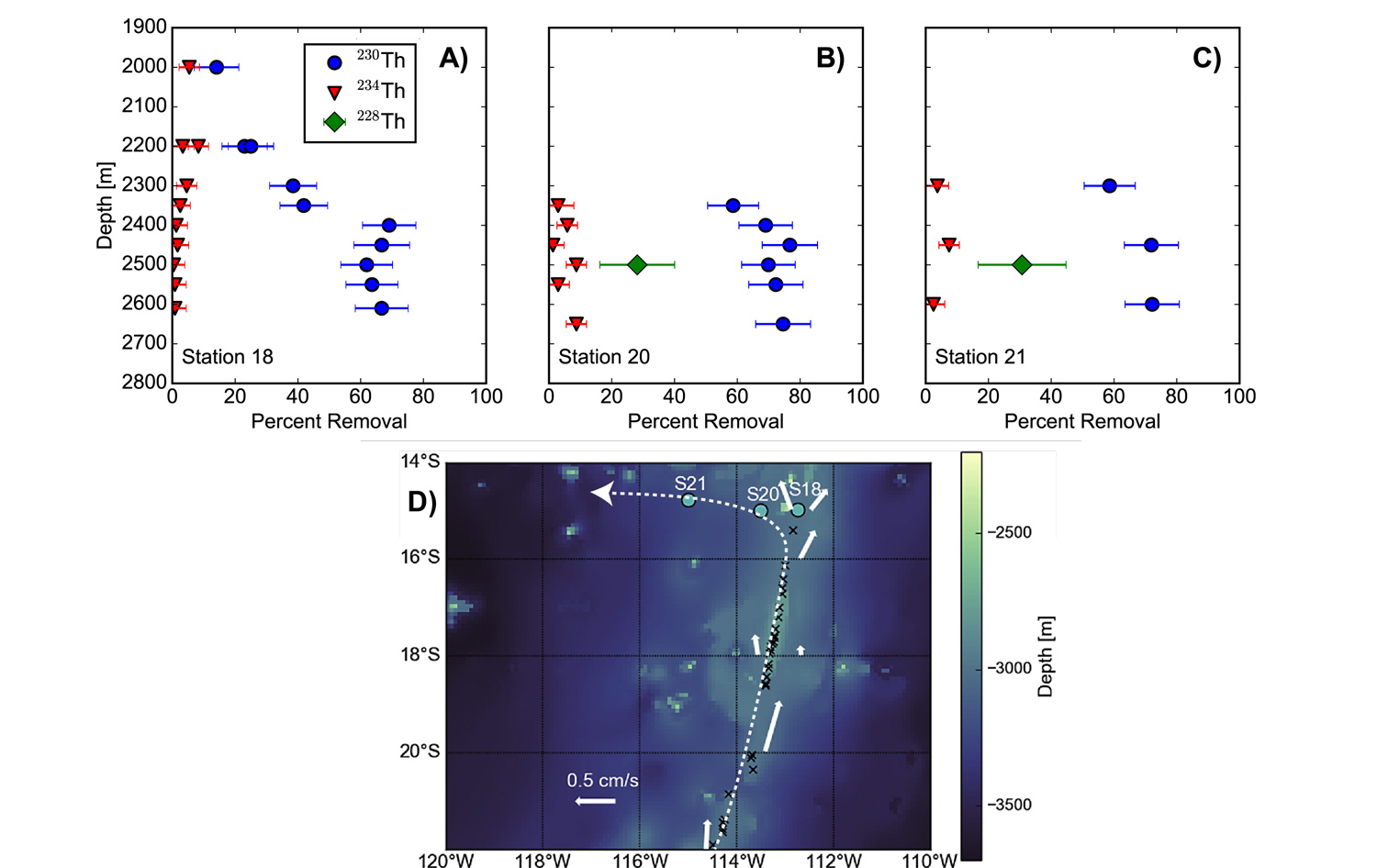
Figure: Depletion observed in three thorium isotopes in the hydrothermal plume observed downstream of the East Pacific Rise on the GEOTRACES GP16 section in the South Pacific Ocean. Plots A), B), and C) show the depletion in each thorium isotope at stations 18 (closest to the ridge axis) to station 21 (furthest from the ridge axis). The depletion increases with increasing half-life of thorium isotope, going from 234Th (half-life = 24.1 days) showing the least depletion, followed by 228Th (half-life = 1.91 years), with 230Th (half-life = 75,587 years) the most depleted. D) Shows the map of the study area, with solid white arrows proportional to current speeds at the plume depth of 2500m, and the white dashed arrow displaying the proposed flowpath of the hydrothermal plume observed in the study, along which thorium is progressively removed from the deep ocean. Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Pavia, F. J., Anderson, R. F., Black, E. E., Kipp, L. E., Vivancos, S. M., Fleisher, M. Q., Charette, M. A., Sanial, V., Moore, W. S., Hult, M., Lu, Y., Cheng, H., Zhang, P., Edwards, R. L. (2019). Timescales of hydrothermal scavenging in the South Pacific Ocean from 234Th, 230Th, and 228Th. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 506, 146–156. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1016/J.EPSL.2018.10.038
