The development of the modern Antarctic Circumpolar Current occurred much later than previously thought!
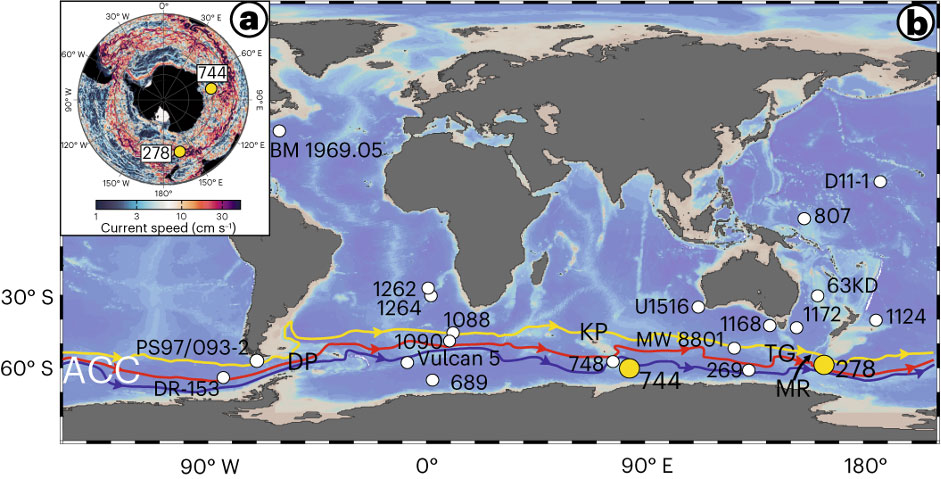
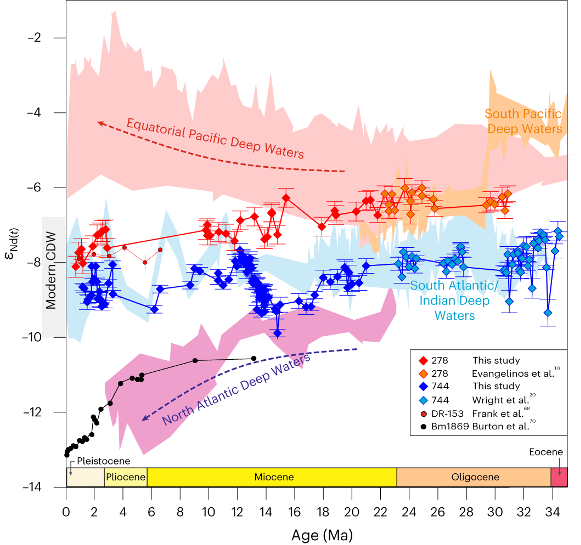
Evangelinos and his colleagues (2024, see reference below) are challenging the widespread belief that the onset of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) was solely triggered by the opening and deepening of Southern Ocean Gateways (Drake Passage, Tasmanian Gateway). They based their conclusions on the analyses of neodymium isotopes (in fish debris, bones and teeth) and sortable silt records from sediment cores collected in the Southwest Pacific and South Indian Oceans spanning the past 31 million years. This exceptional set of proxy-based data reveal the absence of a vigorous, deep-reaching ACC before ∼10 Ma. The authors suggest that the onset of the modern-like, deep-reaching ACC was a result of an enhanced density contrast and the intensification of the South Westerly Winds (SWW) across the Southern driven by the increased Antarctic glaciation following the middle Miocene Climatic Optimum (~14 Ma).
Reference:
Evangelinos, D., Etourneau, J., van de Flierdt, T. et al. Late Miocene onset of the modern Antarctic Circumpolar Current. Nat. Geosci. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41561-023-01356-3
This paper made the cover of the February 2024 issue of the Nature Geoscience Journal (see image below)! Congratulations to all co-authors!

