Surprising conservativity of trace metals along a costal embayment salinity gradient
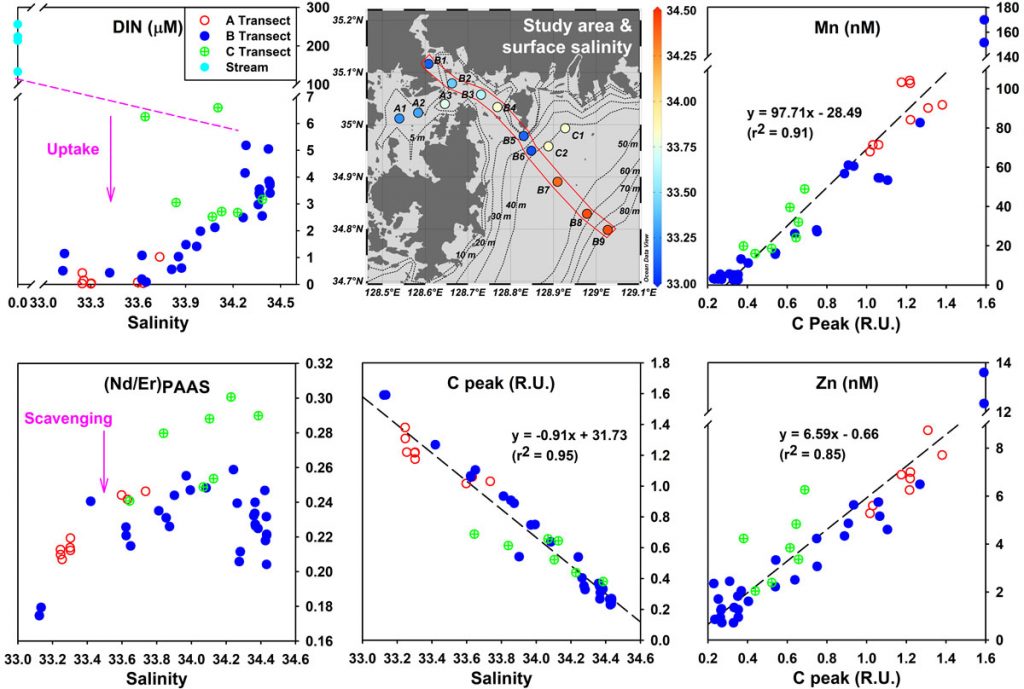
Chen and co-workers (2021, see reference below) analyzed an array of trace metals (manganese, iron, nickel, copper and zinc) together with Rare Earth Elements (REE) in a salinity gradient in the Jinhae Bay, the largest semi-enclosed bay in South Korea. Despite the occurrence of a significant scavenging activity revealed by the REE behaviors and intensive biological removal processes revealed by dissolved inorganic nutrients depletion, these trace elements showed higher concentrations in lower salinity waters and significant positive correlations with terrestrial humic substances. This thorough speciation study led the authors to hypothesize that when associated with terrestrial humic substances, these trace elements survive particle scavenging and biological consumption in the coastal mixing zone. This shuttling effect of terrestrial trace elements by humic substances in a coastal ocean is challenging the current paradigm assessing that trace elements are intensively removed in such salinity gradient.
Reference:
Chen, X., Seo, H., Han, H., Seo, J., Kim, T., & Kim, G. (2021). Conservative behavior of terrestrial trace elements associated with humic substances in the coastal ocean. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.GCA.2021.05.020
