Solute-particle interactions and the enhanced dissolved barium flux from the Ganga River estuary
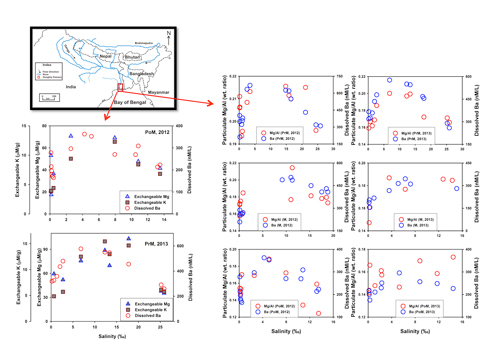
Dissolved and particulate barium (Ba) were investigated in samples that were collected in six periods of contrasting water discharge over two years (2012 and 2013) by Saumik and Dalai (2016, see reference below) in the Ganga (Hooghly) River estuary. The authors thoroughly documented anthropogenic sources and submarine groundwater discharges, which account for less than 2% and 5%, respectively, of the total dissolved Ba discharged annually by this estuary to the oceans. A dominant fraction of dissolved Ba results from desorption of Ba from clay minerals and/or iron-manganese hydroxides in the particulate matter.
The estimates of Ba flux show that annually (1.5–1.9) x 107 moles of Ba is transported by the Hooghly River. Additionally, about (3.6–4.3) x 107 moles of Ba is generated annually in the estuary through ion-exchange and desorption. This means that in the Ganga River estuary, the solute-particle interactions enhance the riverine Ba flux by >300%.
Reference:
Samanta, S., & Dalai, T. K. (2016). Dissolved and particulateBarium in the Ganga (Hooghly) River estuary, India: Solute-particle interactions and the enhanceddissolved flux to the oceans. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 195, 1–28. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2016.09.005
