Slow-spreading ridges could be major oceanic iron contributor
A large dissolved iron- and manganese-rich plume has been detected by Saito and co-authors over the slow-spreading southern Mid-Atlantic Ridge. This discovery calls into question the assumption that deep-sea hydrothermal vents along slow-spreading ridges were negligible contributors to the oceanic iron inventory. This result urges reassessment and a likely increase of the contribution of hydrothermal vents to the supply of iron.
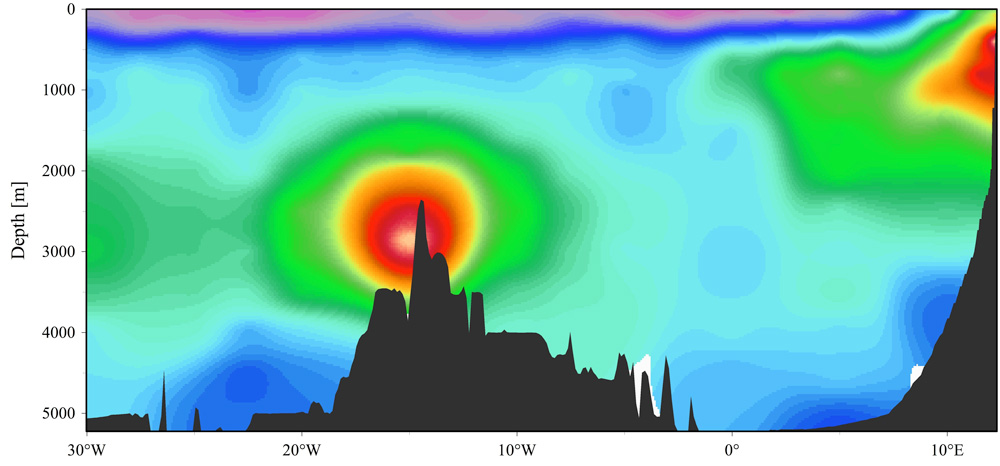
Figure: A zonal section of dissolved iron in the South Atlantic. The higher iron concentrations (in warm colours red, orange) reveal a large plume at ∼2,900 m depth and 2 km in height.
Please click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Saito, Mak A., Abigail E. Noble, Alessandro Tagliabue, Tyler J. Goepfert, Carl H. Lamborg, William J. Jenkins (2013) Slow-spreading submarine ridges in the South Atlantic as a significant oceanic iron source Nature Geoscience 6 (9), 775-770 DOI: 10.1038/ngeo1893
