Scandium: a new oceanic tracer with surprising properties
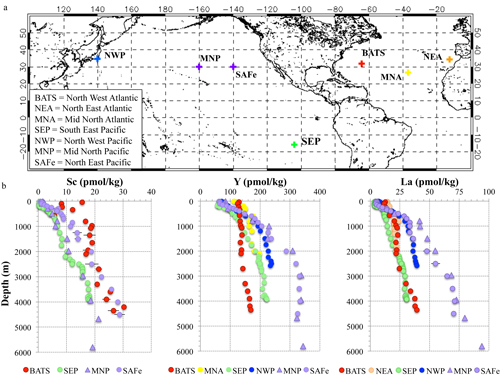
The first modern data set of dissolved scandium (Sc) in the open ocean is presented. Thanks to three GEOTRACES cruises, its distribution is compared between the different oceanic basins. This work also compares the reactivity of Sc with its trivalent periodic table group mates: yttrium (Y) and lanthanum (La) on the one hand, and aluminium (Al) and gallium (Ga) on the other hand.
These distributions and comparisons reveal that scandium is a hybrid-type metal with a residence time on the order of 1000 years. In addition, Sc displays similar particle reactivity to iron, which makes the authors suggest that Sc could help to constrain the non-biogenic part of the iron cycle.
Reference:
Parker, C. E., Brown, M. T., & Bruland, K. W. (2016). Scandium in the open ocean: A comparison with other group 3 trivalent metals. Geophysical Research Letters, 43, 2758–2764. doi:10.1002/2016GL067827
