Results from the GEOTRACES cruise section GIPY11
An interesting comparison of data of dissolved barium (Ba) and data of dissolved aluminium (Al) and silicate (Si) collected onboard the GEOTRACES cruise GIPY11 (ARK-XXII/2 Polarstern expedition) is presented in the article of Roeske and colleagues (Roeske et al, 2012). This comparison is used to distinguish between signals produced by the regeneration of sinking particles and signals derived from entrainment of shelf waters, adding to the analysis of Al and Si data of the same cruise by Middag et al. (2009). The two papers investigate whether the relationships between Ba, Si and Al differ between water masses and between the various deep Arctic Basins, and whether these differences can help us to infer deep water circulation and shelf water inputs.
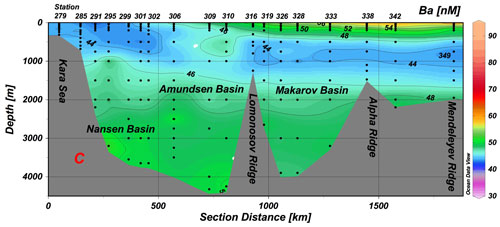
Figure: Distribution of Ba on section C, which reaches from the Kara Sea at 81.25°N to the Alpha Ridge at 84.5°N. Isolines are at 2 nM intervals. Source: Marine Chemistry.
References:
Middag, R., de Baar, H.J.W., Laan, P., Bakker, K., (2009). Dissolved aluminium and the silicon cycle in the Arctic Ocean. Marine Chemistry 115, 176-195
Roeske T., Rutgers vd Loeff M., Middag R, Bakker K. (2012), Deep water circulation and composition in the Arctic Ocean by dissolved barium, aluminium and silicate, Marine Chemistry 132-133, (56-67).
