Particle distribution in repeated ocean sections and sediment resuspension
This is the first compilation of an expansive data base of transmissometer data on a decadal period of time. More than 7376 stations have been analyzed for “cp” value, a proxy for particle concentrations, by Gardner and co-workers (2018, see reference below). Full water-column sections confirm that particle concentrations are higher in surface waters, decrease rapidly below 200 m, most often down to the seafloor. However, cloudy near-bottom waters, known as “benthic nepheloid layers”, are generated by sediment erosion and resuspension at specific geographic areas. These locations are directly linked to energetic surface dynamics that produce regions of high Eddy Kinetic Energy (EKE). More fascinating, however, is the decadal persistence of this close surface-to-deep connection. We invite you to read this very interesting article!
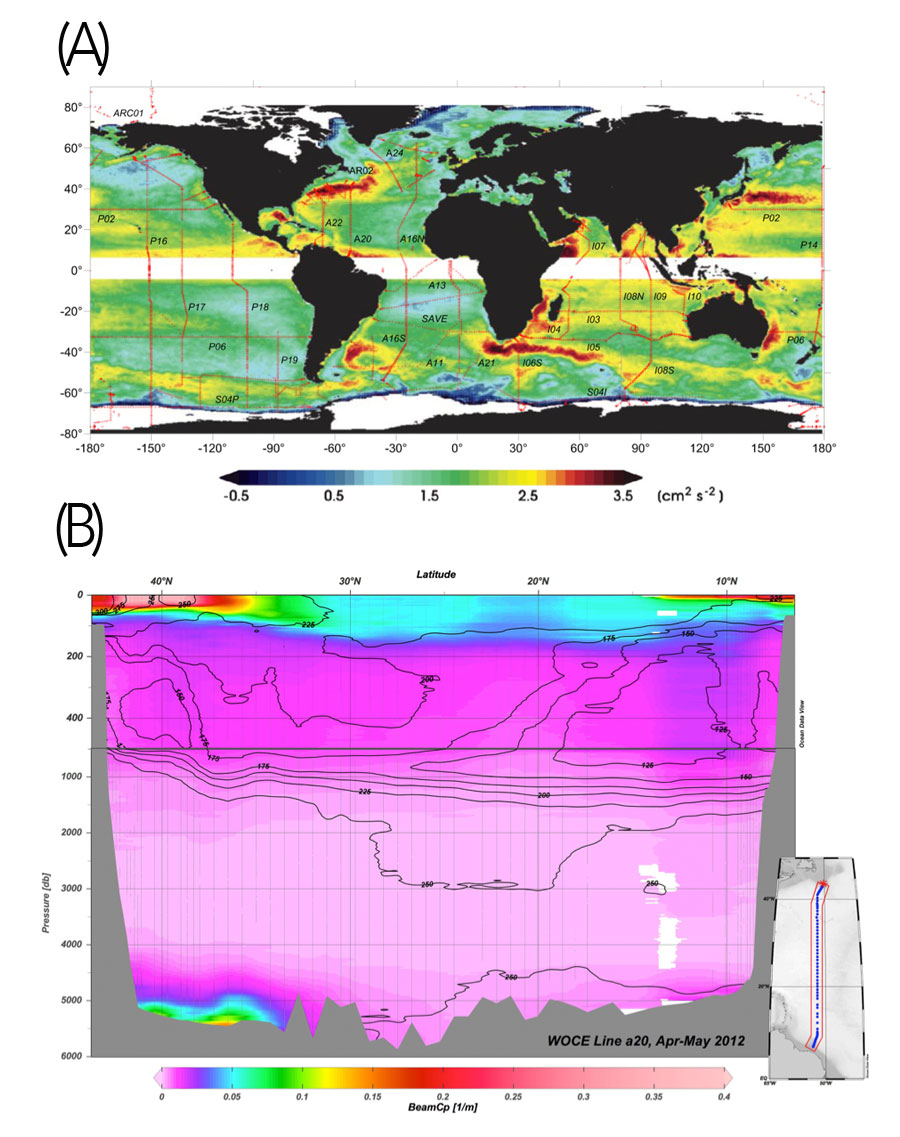 Figures: (A) Map of log of surface eddy kinetic energy (modified from Dixon et al., 2011) with cp transects indicated. (B) Section of cp (proxy for particle concentration) along 53° W in spring, 2012 in the Western North Atlantic. Black contours are dissolved oxygen (µmol kg-1). Click here to view the figure larger.
Figures: (A) Map of log of surface eddy kinetic energy (modified from Dixon et al., 2011) with cp transects indicated. (B) Section of cp (proxy for particle concentration) along 53° W in spring, 2012 in the Western North Atlantic. Black contours are dissolved oxygen (µmol kg-1). Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Gardner, W. D., Mishonov, A. V., & Richardson, M. J. (2018). Decadal Comparisons of Particulate Matter in Repeat Transects in the Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Ocean Basins. Geophysical Research Letters. http://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL076571
