New strategy to evaluate trace element fluxes to the ocean from aerosols
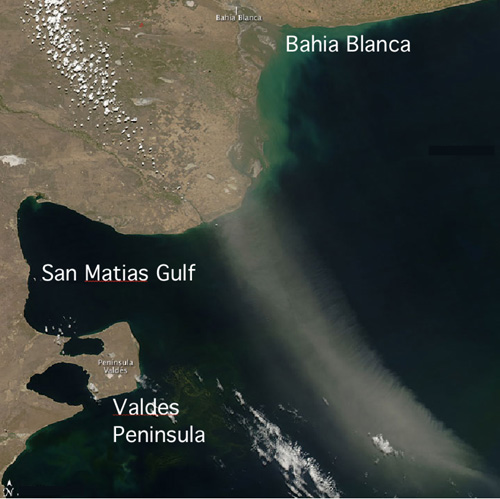 Scientists participating in GEOTRACES have developed a new strategy to evaluate trace element fluxes to the ocean from aerosols (Hsieh et al, 2011). The new approach uses the common geochemical behaviour of two isotopes of the same chemical element (thorium;Th), whose sources to the surface seawater are totally different (and independent). 230Th is a decay product of the homogeneously distributed 234U in seawater and provides a measure of the residence time of Th element in surface waters. This residence time is applied to 232Th content of the same water column. Because 232Th derives from dust from weathered rocks and enters the ocean surface waters in aerosols, knowing its amount and residence time allows reconstruction of the input of aerosol to the ocean surface. Hsieh and co-workers successfully applied this approach in the central Atlantic Ocean, including an assessment of aerosol fluxes associated with the dust plume blowing from South American over the South Atlantic (see photo).
Scientists participating in GEOTRACES have developed a new strategy to evaluate trace element fluxes to the ocean from aerosols (Hsieh et al, 2011). The new approach uses the common geochemical behaviour of two isotopes of the same chemical element (thorium;Th), whose sources to the surface seawater are totally different (and independent). 230Th is a decay product of the homogeneously distributed 234U in seawater and provides a measure of the residence time of Th element in surface waters. This residence time is applied to 232Th content of the same water column. Because 232Th derives from dust from weathered rocks and enters the ocean surface waters in aerosols, knowing its amount and residence time allows reconstruction of the input of aerosol to the ocean surface. Hsieh and co-workers successfully applied this approach in the central Atlantic Ocean, including an assessment of aerosol fluxes associated with the dust plume blowing from South American over the South Atlantic (see photo).
This new method is now being incorporated into GEOTRACES cruises across the Atlantic and beyond.
Reference:
Yu-Te Hsieh, Gideon M. Henderson, Alexander L. Thomas (2011), Combining seawater 232Th and 230Th concentrations to determine dust fluxes to the surface ocean Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 312 (3-4) DOI: 10.1016/j.epsl.2011.10.022
