New method for measuring simultaneously trace metal concentrations on a very small volume of seawater
An automated, on-line extraction, flow-injection inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) method is presented by Lagerström and co-authors for simultaneous determination of manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni), copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn) in open ocean seawater samples. This fully automated commercially available system buffers the pH of the samples on-line and extracts the trace metals from 9 mL of seawater onto a chelation resin column, which is then eluted directly into a magnetic sector ICP-MS. Precision of 1–3% (RSD) and very good agreement with reference consensus values are obtained for most of the elements in less than 9 min per analysis.
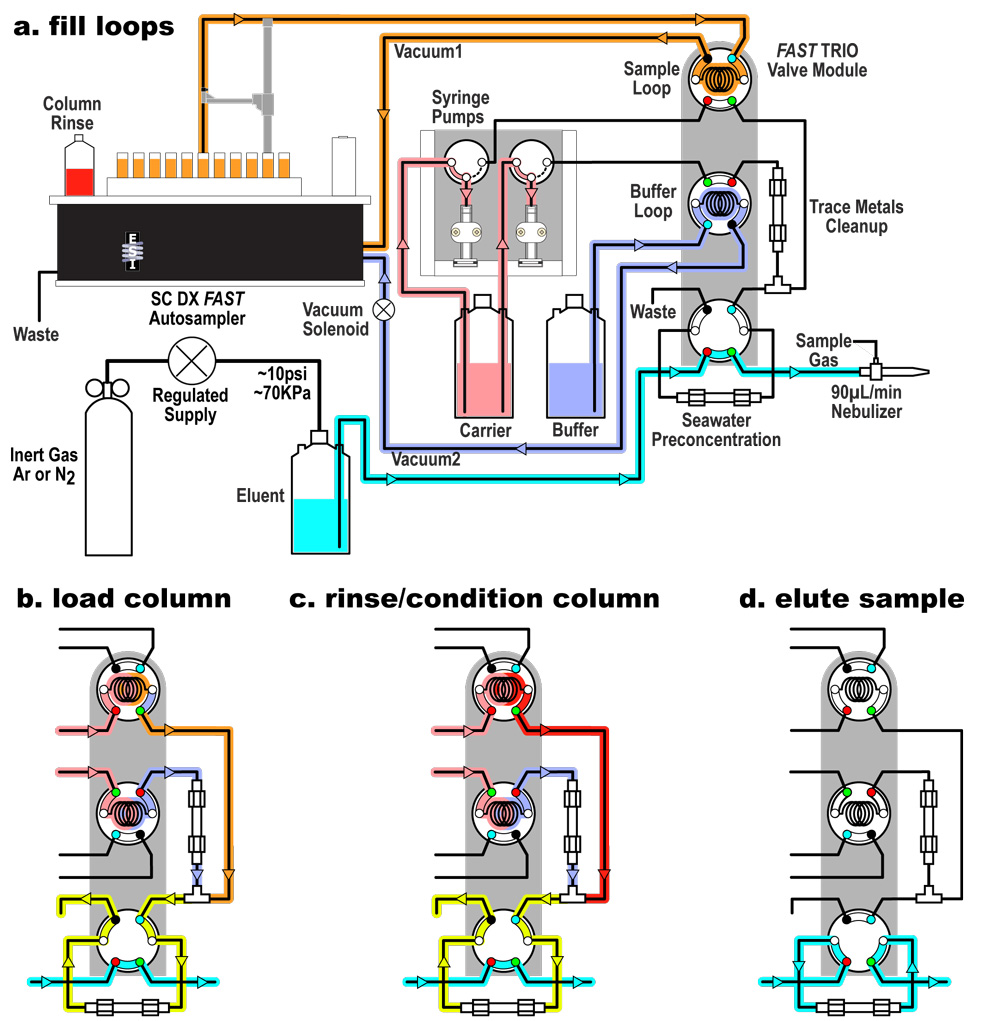
Figure: This figure shows the on-line flow injection system. Click here to view the figure in high resolution.
Reference:
M.E. Lagerström, M.P. Field, M. Séguret, L. Fischer, S. Hann, R.M. Sherrell Automated on-line flow-injection ICP-MS determination of trace metals (Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu and Zn) in open ocean seawater: Application to the GEOTRACES program, Marine Chemistry, Volume 155, 20 September 2013, p. 71–80 DOI: 10.1016/j.marchem.2013.06.001 Click here to access the paper.
