Confrontation of two models to constrain the hydrothermal iron contribution to the Southern Ocean export production
Tracing the pathway and impact of hydrothermal dissolved iron (HDFe) up to the upper oceanic layers is important, since earlier works suggested that HDFe supports up to 15% of the surface export production. Input HDFe is quantified using helium-3 (3He) supply, taken as a conservative tracer of hydrothermal origin. However, this distribution is different if it is modelled based on the ridge spreading rate (spreading model) or if the ridge 3He source is optimised using water column 3He measurements in a data-constrained inverse model (inverse model). In particular, the inverse model has a strong reduction in He input from Southern Ocean ridges, which directly challenges the role of hydrothermal Fe in supporting export production and the regional biological carbon pump in this area.
Here, Alessandro Tagliabue and his co-workers (2022, see reference below) compare the HDFe simulated by both models. They reveal that despite having the same total hydrothermal iron (Fe) supply as the spreading experiment, spatial differences in the inverse experiment cause a 4–5 fold reduction in the contribution of hydrothermal dissolved iron (DFe) in the upper 200 m. Consequently, the Southern Ocean carbon export production signal associated with hydrothermal Fe declines substantially during the inverse experiment. However, confronting with new DFe data collected along the GS01 GEOTRACES section south of Tasmania, it is revealed that only spreading input experiment is able to reproduce the observed level of DFe enrichment above Southern Ocean ridges. This suggests that the greater impact of hydrothermal Fe on the biological carbon pump from the spreading experiment is more consistent with DFe observations. Then, the authors discuss the implications for HDFe residence times in the Southern Ocean.
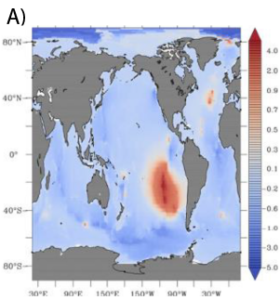
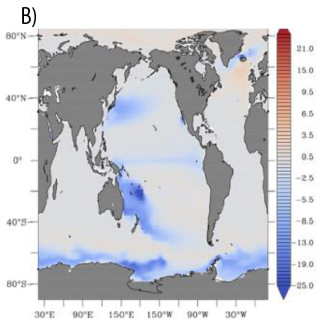
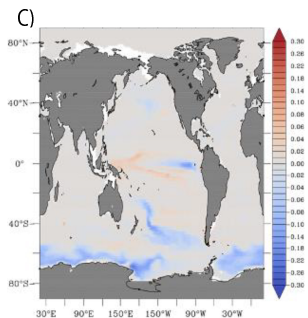
Figure: The difference on the impact of hydrothermal vents of the concentration of dissolved iron between the two models (inverse and spreading), A) over the full-water column (in mmol m–2), for B) the impact of hydrothermal vents on the concentration of dissolved iron over the upper 200 m (in μmol m–2) and for c) the impact of hydrothermal Fe on the biological carbon pump at 100 m (mol C m–2 yr–1).
Reference:
Tagliabue, A., Bowie, A. R., Holmes, T., Latour, P., van der Merwe, P., Gault-Ringold, M., Wuttig, K., & Resing, J. A. (2022). Constraining the Contribution of Hydrothermal Iron to Southern Ocean Export Production Using Deep Ocean Iron Observations. Frontiers in Marine Science, 9. Access the paper:10.3389/fmars.2022.754517
