Loihi Seamount, hydrothermal Helium-3 and dissolved iron sources and their dispersion within the Pacific Ocean
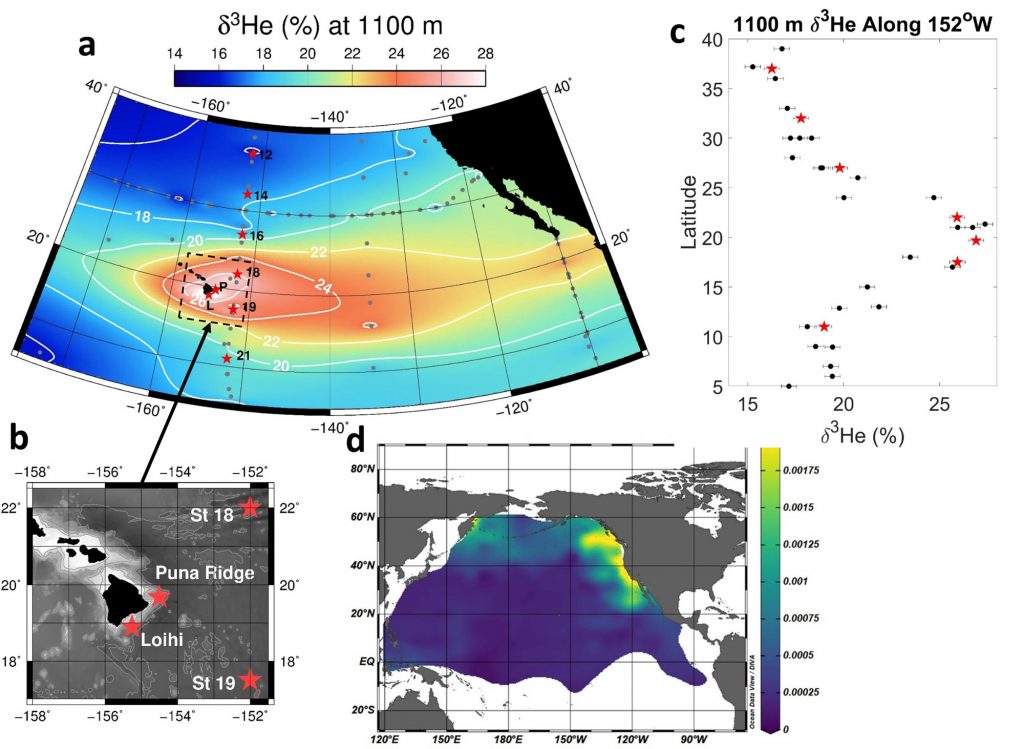
As part of the GEOTRACES cruise GP15, Jenkins and co-workers (2020, see reference below) observed large water column anomalies in helium isotopes and trace metal concentrations above the Loihi Seamount (~19°N, 154°W) that extends along the GP15 track for hundreds of kilometers. Expanding their data with historical ones, they observe that the Loihi Helium-3 (3He) and dissolved iron (dFe) “signal” was propagating at depth of 1100 m within ∼100 – 1000 km of Loihi, characterized by a distal dFe:3He ratio of ∼4 ×106. Contrastingly, no major methane input was observed. Modeling the regional circulation allowed these authors to estimate a hydrothermal 3He source from Loihi of 10.4 ±4.2 mol a−1 and a corresponding dFe flux of ∼40 Mmol a−1. On a larger scale, they simulate that the Loihi-influenced waters (enriched in He and Fe) eventually upwell along the west coast of North America, also extending around 1000 km into the northwest Pacific Ocean, which could play a role in fertilizing the subpolar North Pacific Ocean.
Reference:
Jenkins, W. J., Hatta, M., Fitzsimmons, J. N., Schlitzer, R., Lanning, N. T., Shiller, A., Buckley, N. R., German, C. R., Lott, D. E., Weiss, G., Whitmore, L., Casciotti, K., Lam, P. J., Cutter, G. A., Cahill, K. L. (2020). An intermediate-depth source of hydrothermal 3He and dissolved iron in the North Pacific. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 539, 116223. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.epsl.2020.116223
