Important warning about the uncertainties affecting results of dissolved iron concentration measurements in seawater using flow-injection with chemiluminescence detection
Flow-Injection with Chemiluminescence (FI-CL) is a procedure commonly applied in the framework of the GEOTRACES cruises because of its portability and hence suitability for shipboard deployment.
Following the Guide for Uncertainty Measurement (GUM) approach, Floor and colleagues propose dedicated mathematical equations allowing the estimation of measurement uncertainties. They apply their model to estimate combined uncertainties obtained for analyses of seawater reference materials (SAFe and GEOTRACES).
This thorough and rigorous examination shows that the final uncertainty of the measurement results using FI-CL in the present protocol configuration cannot be better than 10–15% for seawater samples containing 0.5–1 nmol/kg of dissolved iron (Fe).
This uncertainty might be larger at sea, under more challenging conditions. The most influential sources of uncertainty are the uncertainty on the calibration slope and the lack of stability during the analytical sequence, see figures below).
Authors clearly consider that uncertainty estimations based on the intensity repeatability alone, as is often done in FI-CL studies, is not a realistic estimation of the overall uncertainty of the measurement procedure.
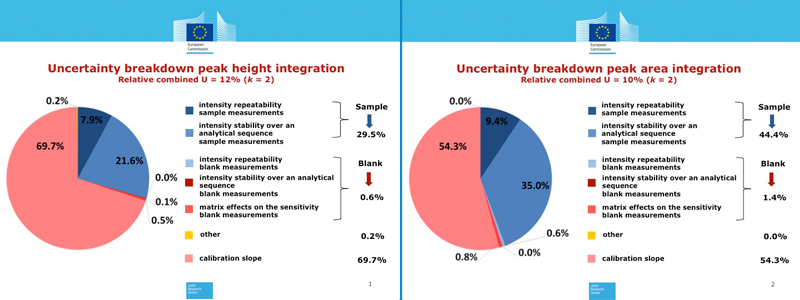
Figures: Combined uncertainty budget estimated for measurements corresponding to signal peak height integration (left, rel. U = 12%, k = 2)
and to signal peak area integration (right, rel. U = 10%, k = 2). Click here to download the figures.
Reference:
Floor, G. H., Clough, R., Lohan, M. C., Ussher, S. J., Worsfold, P. J. and Quétel, C. R. (2015), Combined uncertainty estimation for the determination of the dissolved iron amount content in seawater using flow injection with chemiluminescence detection. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods, 13: 673–686. doi:10.1002/lom3.10057
