Icebergs; a huge but highly variable source of iron to the ocean
Icebergs have been speculated to constitute one of the largest fluxes of iron (Fe) into the polar oceans since the 1930s and thus recent increases in ice discharge around the world could potentially change Fe availability in the ocean. But how much Fe is in an iceberg? As part of an international collaboration involving several cruises over the past 5 years including the GEOTRACES Fram Strait GN05 section Hopwood et al., (2019, see reference below) report the concentrations of Fe in ice from over 10 glaciated regions around the world. The global mean iceberg Fe content is found to be similar to, or slightly higher than, limited earlier estimates. However, a critical insight is the highly uneven distribution of this Fe with the ‘dirtiest’ 4% of samples collected accounting for over 90% of the cumulative Fe. Investigating how these ‘dirty’ layers are formed and their fate in the ocean is therefore essential to determining the significance of icebergs for marine primary production.
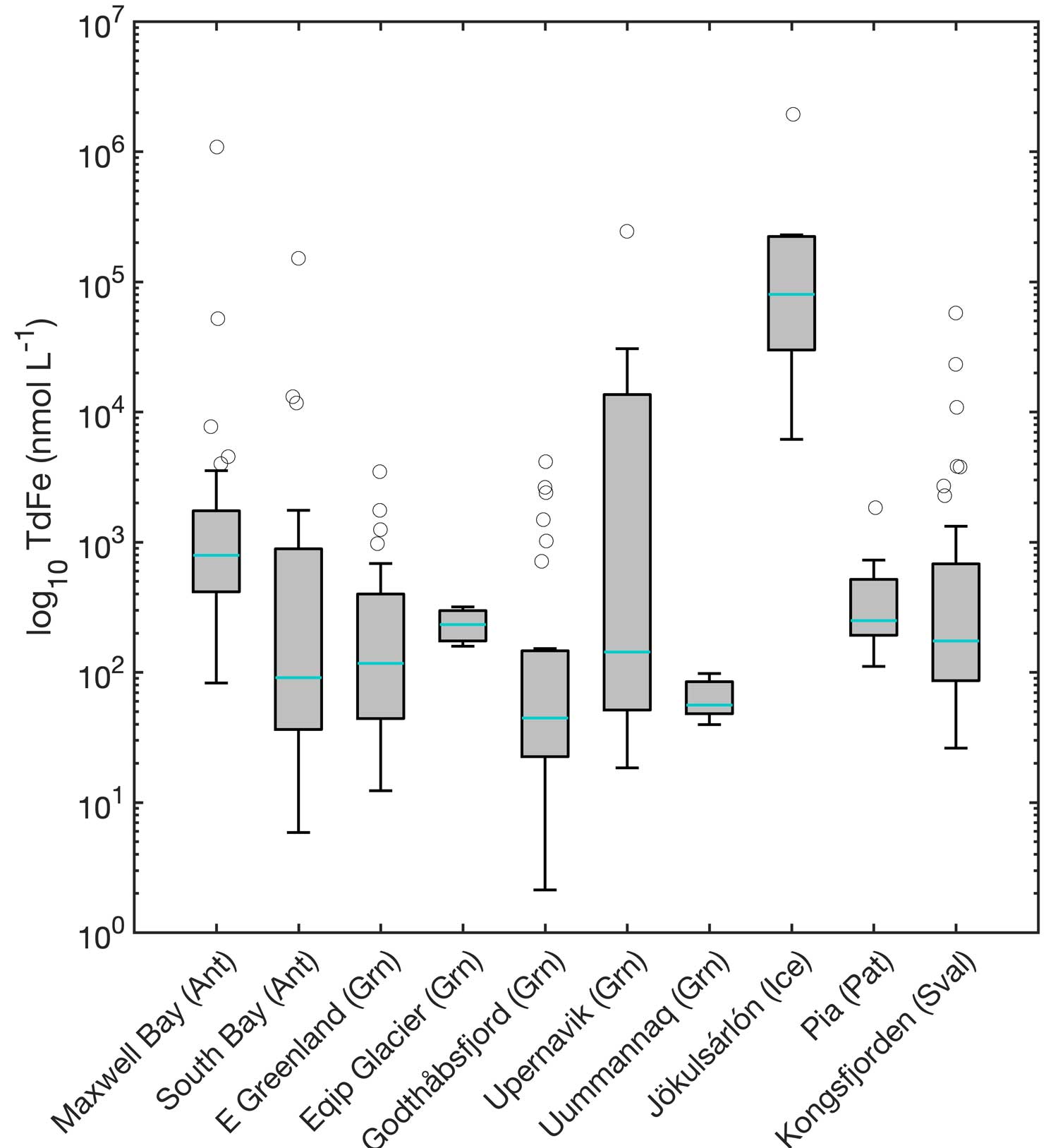
Figure: Ice from around the world is found to have a highly variable total dissolvable Fe content ranging from 2 nM to 2 mM.
Reference:
Mark J. Hopwood, Dustin Carroll, Juan Höfer, Eric P. Achterberg, Lorenz Meire, Frédéric A. C. Le Moigne, Lennart T. Bach, Charlotte Eich, David A. Sutherland & Humberto E. González, (2019) High variability is evident even within individual geographic regions. Reference: Highly variable iron content modulates iceberg-ocean fertilisation and potential carbon export, Nature Communications, 10, 5261 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-13231-0
