High mesopelagic carbon remineralization traced by particulate biogenic barium in the North Atlantic Ocean
The high resolution section of particulate “excess Ba” (Baxs) measured by Lemaitre and co-authors (2018, see reference below) along the GEOVIDE GA1 section (R/V Pourquoi Pas? spring 2014) confirmed the ability of this parameter as proxy of the particulate organic carbon (POC) remineralization. Despite their importance for the biological pump quantification, POC remineralization data are still very scarce in the world ocean (see figure B below). Lemaitre’s work is a major contribution: besides validating the relationship between Baxs and oxygen consumption, it revealed significant remineralization rates at the time and location of the cruise, allowing establishing a biological pump scheme along the section (see figure C below). The link between the estimated POC export fluxes and the surface ecosystems is also discussed.
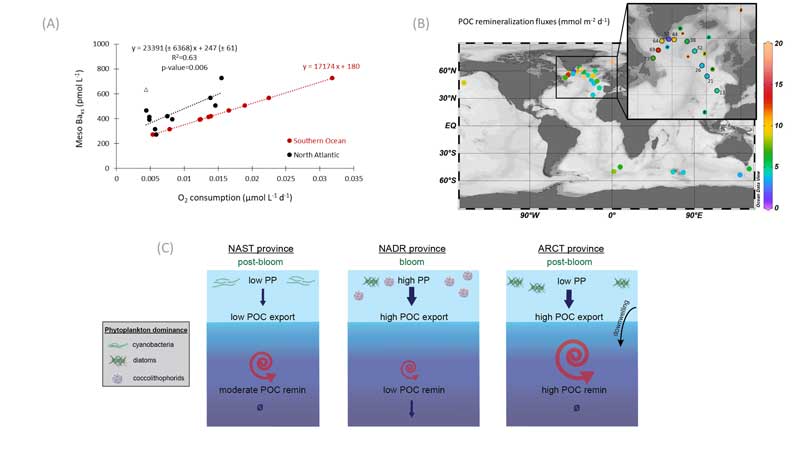 Figure: (A) Relationship of the mesopelagic Baxs concentration versus the O2 consumption rate using the Southern Ocean transfer function (Dehairs et al., 1997) and the transfer function obtained in this study for the North Atlantic. (B) Summary of published POC remineralisation fluxes in the world ocean. (C) General schematic of the biological carbon pump in different provinces of the North Atlantic during GEOVIDE. Click here to view the figure larger.
Figure: (A) Relationship of the mesopelagic Baxs concentration versus the O2 consumption rate using the Southern Ocean transfer function (Dehairs et al., 1997) and the transfer function obtained in this study for the North Atlantic. (B) Summary of published POC remineralisation fluxes in the world ocean. (C) General schematic of the biological carbon pump in different provinces of the North Atlantic during GEOVIDE. Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Lemaitre, N., Planquette, H., Planchon, F., Sarthou, G., Jacquet, S., García-Ibáñez, M. I., Gourain, A., Cheize, M., Monin, L., André, L., Laha, P., Terryn, H., Dehairs, F. (2018). Particulate barium tracing of significant mesopelagic carbon remineralisation in the North Atlantic. Biogeosciences, 15(8), 2289–2307. http://doi.org/10.5194/bg-15-2289-2018
