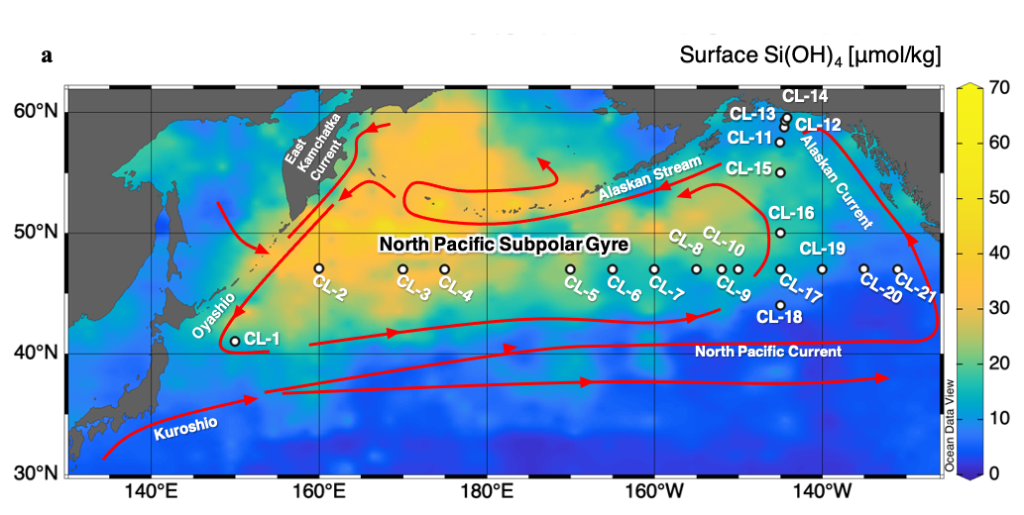
East-West contrasting fate and anthropogenic inputs for dissolved trace metals in the Subarctic Pacific Ocean
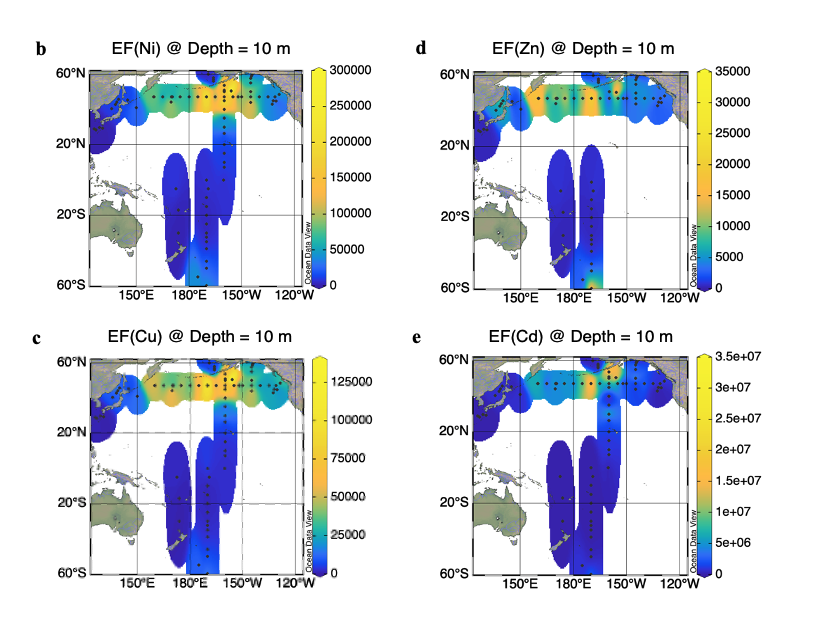
Chan and co-authors (2025, see reference below) report the full-depth distribution of dissolved (d) nickel (Ni), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), and cadmium (Cd) in the North Pacific Ocean. These trace metals (TM) are bioactive and known as «nutrient-type elements». However, this study highlights contrasting east–west differences in their distribution in the subarctic Pacific Ocean. While the solid linear relationship between dCd and phosphate (PO4) confirms that both nutrients are tight by a concurrent influence of ocean circulation and biogeochemical cycling, other TM shows variable influences of scavenging, remineralization, bottom or margin inputs and transport. The ratio between dTM and PO4 proves that the effect of scavenging is increasing in the order of Cd < Ni < Zn < Cu < Fe, processes leading to a distinct east–west distributions in the upper water. The depletion of dZn is severe in the eastern subarctic Pacific, while the calculation of Enrichment Factors (EF) reveals high anthropogenic atmospheric input of trace in the subarctic Pacific under the westerly wind zone.
Reference:
Chan, C.-Y., Zheng, L., & Sohrin, Y. (2025). The behaviour of nickel, copper, zinc, and cadmium in the subarctic Pacific Ocean: East–West differences. Journal of Oceanography. Access the paper:10.1007/s10872-025-00746-y
