Determining simultaneously iron, zinc and cadmium isotopes in small volumes of seawater is possible now!
The first simultaneous method for the determination of these three isotope systems in seawater has been published. This method is designed for use on only a single litre of seawater representing a 1–20 fold reduction in sample size and a 4–130 decrease in blank compared to previously reported methods. The procedure yields data with high precision for all three elements, allowing estimation of natural variability in the oceans, which spans 1–3‰ for all three isotope systems. Simultaneous extraction and purification of three metals makes this method ideal for high-resolution, large-scale endeavours such as the GEOTRACES programme.
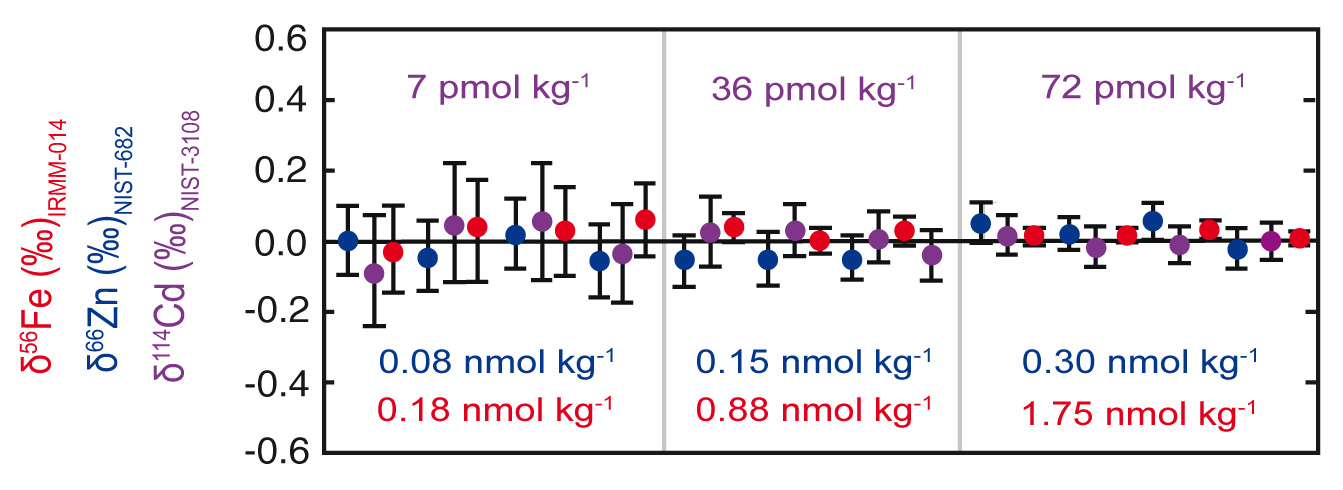
Figure: ‘Metal-free’ seawater doped with varying concentrations of ‘zero’ isotope standards, processed through the simultaneous method, and then analysed by double spike MC-ICPMS for Fe, Zn and Cd isotope ratios. All values were determined within 2 sigma error (error bars shown) of zero.
Reference:
Tim M. Conway, Angela D. Rosenberg, Jess F. Adkins, Seth G. John (2013), A new method for precise determination of iron, zinc and cadmium stable isotope ratios in seawater by double-spike mass spectrometry, Analytica Chimica Acta, Volume 793, Pages 44-52, DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2013.07.025. Click here to access the paper.
