Aluminium, manganese, iron, cobalt, and lead display contrasting fate along north–south and east–west sections in the North Pacific Ocean
Chan and co-authors report the distribution of the dissolved and labile particulate aluminium (Al), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), and lead (Pb) in the subarctic Pacific Ocean during the GEOTRACES Japan KH-17-3 cruise and along the 47° N zonal transect (GEOTRACES GP02 Line). This provides a comprehensive view of dissolved and particulate trace metal distribution in the subarctic Pacific Ocean:
- The trace metals behave differently along the north–south and east–west transects of the cruise. An intensive boundary scavenging occurs off the coast of Alaska -covering ca 250 km width-, limiting the impact of the continental sources (fluvial and sediment inputs) in this area.
- At the easternmost station, the effect of the hydrothermal activity of the Juan de Fuca Ridge was detected.
- Isopycnal transport of dMn and lpMn from the Okhotsk and Bering Seas to the western subarctic Pacific is also discussed.
- Last but not least, this work proposes a temporal study of Pb distributions, which confirm that declining anthropogenic emissions of Pb resulted in a decadal change in dPb in the middle of the subarctic gyre.
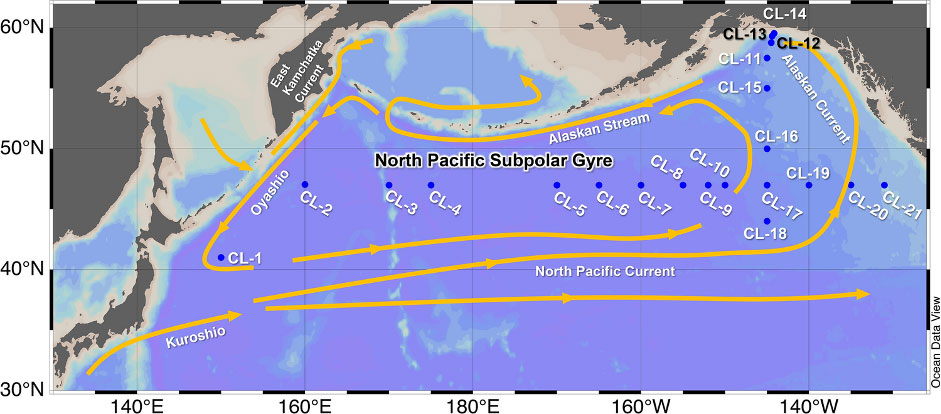
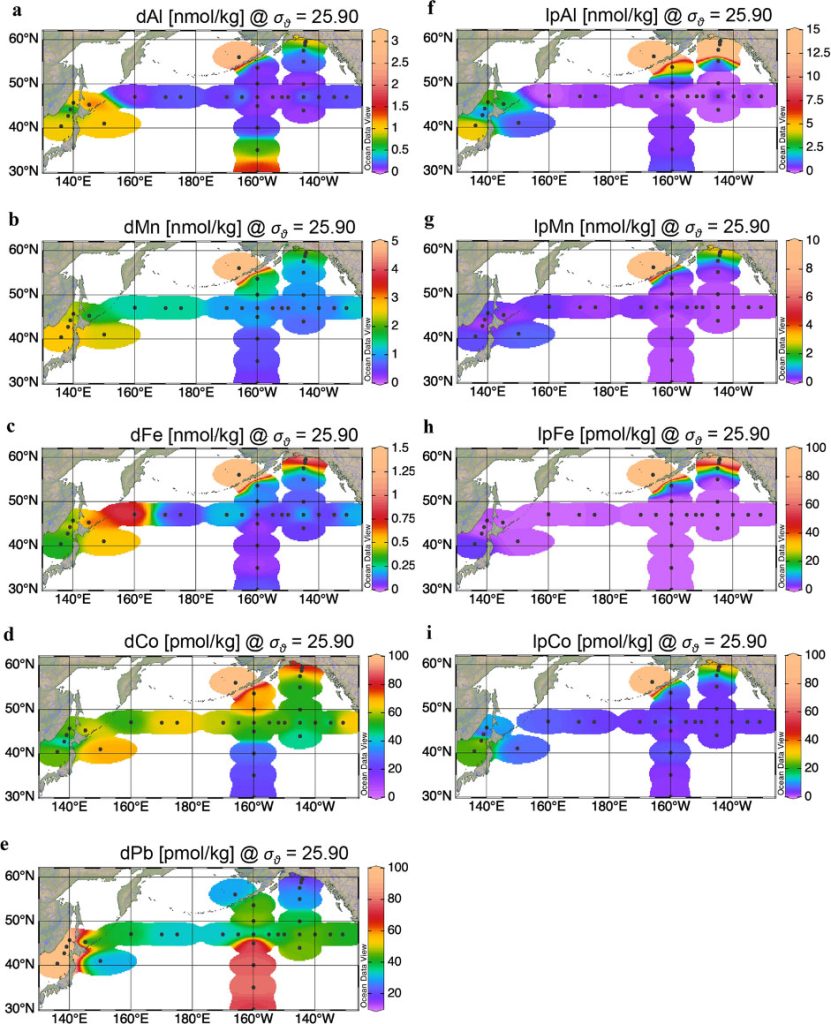
The depth of this isopycnal surface is ~ 30 m in the west and ~ 120 m in the east generally below the surface mixed layer. Dissolved and particulate Al, Mn, Fe, and Co show isopycnal transport from the Okhotsk and Bering Seas to the western subarctic Pacific. In the Gulf of Alaska, boundary scavenging limits the spread of the continental supply of metals. Dissolved Pb has a distinct isopycnal distribution that reflects the anthropogenic aerosol supply from Asian countries and Russia.
Reference:
Chan, C.-Y., Zheng, L., & Sohrin, Y. (2024). The behaviour of aluminium, manganese, iron, cobalt, and lead in the subarctic Pacific Ocean: boundary scavenging and temporal changes. Journal of Oceanography. Access the paper: 10.1007/s10872-023-00710-8
