Changing the cadmium : phosphorus paradigm?
The well-established strong linear relationship linking dissolved cadmium (Cd) and phosphorus (P) concentrations in seawater is at the origin of the attraction of Cd as a proxy for PO4 in the paleocean. However, exploring the dissolved Cd and PO4 distributions in the ocean, Quay and co-workers (2015, see reference below) show that the Cd/P of particles exported from the surface ocean doubles in high-nutrients low chlorophyll (HNLC) regions. They also demonstrate that Cd/PO4 variations in the surface ocean and deep sea depend on Cd/P of degraded particles. Using a box model, they present evidence that past changes in HNLC conditions would change the Cd-PO4 relationship in deep sea… which has to be considered in paleo-reconstructions!
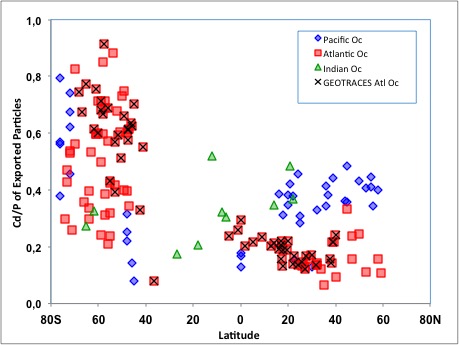
Figure: The meridional and interbasin trends in the estimated Cd/P ratio of particles exported from the surface ocean. The Cd/P of exported particles is a primary factor controlling the spatial variations dissolved Cd/P in the surface ocean and in the deep sea where particles are degraded.
Reference:
Quay, P., Cullen, J., Landing, W., & Morton, P. (2015). Processes controlling the distributions of Cd and PO4 in the ocean. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 29(6), 830–841. doi:10.1002/2014GB004998
