Breaking down disciplinary silos in marine sciences, a key to climate forecasting
In a Nature comment, Alessandro Tagliabue (2023, see reference below) exposes how ocean modelling must evolve to take the biological complexity of the surface ocean into account. There is an urgent need to understand how marine microbes are affected by the climate change, allowing us to forecast the future state of the oceans. Indeed, there is little confidence today on predictions of how marine microbes will react to global changes.
After an analysis of the pro and cons of the biogeochemical models, the mechanistic metabolic models, or the exploitation of statistics, Tagliabue advocates that researchers in mathematical and ecological theory should break down their disciplinary silos, to improve and share their fundamental knowledge and benefit from the growing computing power to develop new generations of models. These models allowing a considerable step forward in our ability to overcome the ocean complexity and to forecast it.
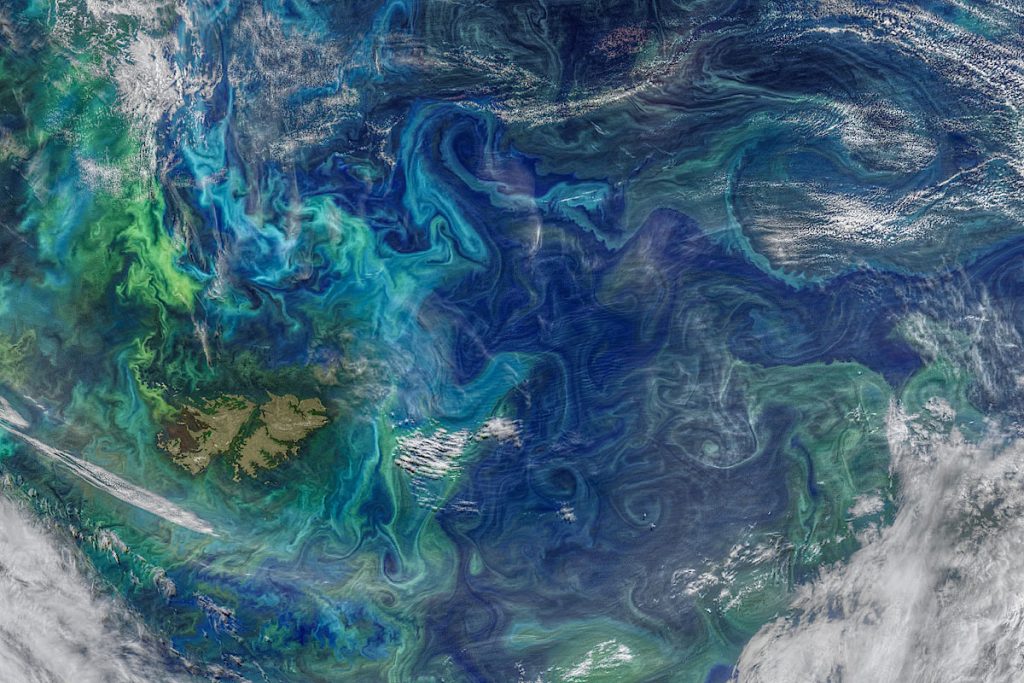
Credit: NASA Ocean Biology Processing Group. Collected by the two VIIRS sensors (NOAA 20 and Suomi-NPP) on January 5, 2021. NASA Ocean Biology Distributed Active Archive Center. Retrieved from https://oceancolor.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/738/
Reference:
Tagliabue, A. (2023). ‘Oceans are hugely complex’: modelling marine microbes is key to climate forecasts. Nature, 623, 250–252. Access the paper:10.1038/d41586-023-03425-4
