Arctic rivers are discharging organic matter enriched in mercury to the Labrador Sea
In the framework of GEOVIDE-GEOTRACES GA01 cruise (spring 2014), Cossa and co-workers (see reference below) measured the first high-resolution mercury (Hg) distribution pattern along a transect from Greenland to Labrador coasts. An interesting feature is the observation of Hg enrichment originating from fluvial sources in the Canadian Arctic Archipelago waters. This excess Hg is transferred southward, in surface waters with the Labrador Current, and at depth with the lower limb of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation via the Deep Western Boundary Current. The authors underline that global warming could accelerate permafrost thawing in a near future, increasing the Hg discharge by the Arctic rivers.
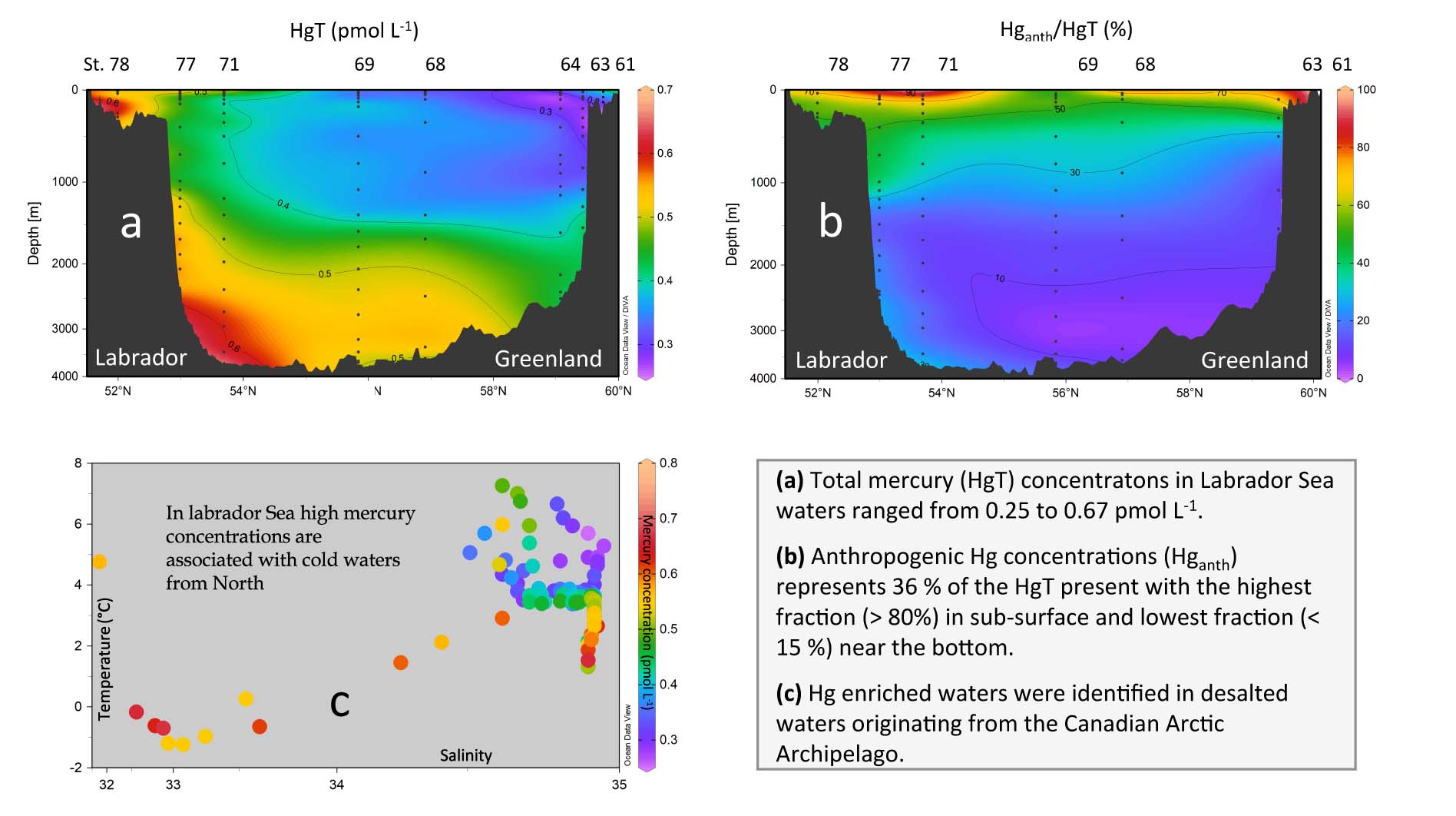 Figure: (a) Total mercury (HgT) concentratons in Labrador Sea waters ranged from 0.25 to 0.67 pmol L-1; (b) Anthropogenic Hg concentrations (Hganth) represents 36 % of the HgT present with the highest fraction (> 80%) in sub-surface and lowest fraction (< 15 %) near the bottom; (c) Hg enriched waters were identified in desalted waters originating from the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Please click here to view the image larger.
Figure: (a) Total mercury (HgT) concentratons in Labrador Sea waters ranged from 0.25 to 0.67 pmol L-1; (b) Anthropogenic Hg concentrations (Hganth) represents 36 % of the HgT present with the highest fraction (> 80%) in sub-surface and lowest fraction (< 15 %) near the bottom; (c) Hg enriched waters were identified in desalted waters originating from the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. Please click here to view the image larger.
Reference:
Cossa, D., Heimbürger, L. E., Sonke, J. E., Planquette, H., Lherminier, P., García-Ibáñez, M. I. Pérez, F.F., Sarthou, G. (2018). Sources, cycling and transfer of mercury in the Labrador Sea (Geotraces-Geovide cruise). Marine Chemistry, 198, 64–69. http://doi.org/10.1016/J.MARCHEM.2017.11.006
