Arctic mercury export flux with marine particles higher than anticipated
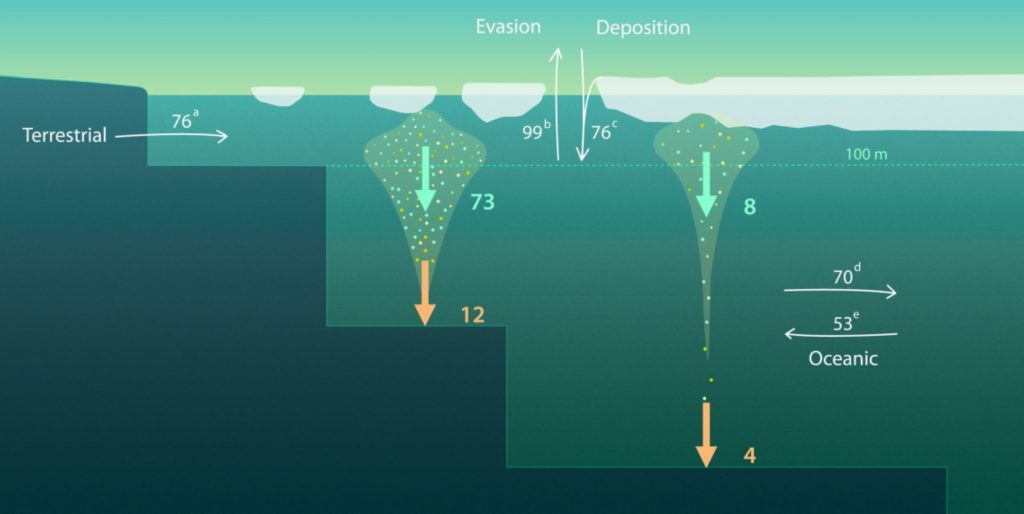
In the ocean, the residence time of mercury (Hg), is largely driven by two removal mechanisms: evasion to the atmosphere and downward export flux with settling particles. The later was particularly poorly constrained in the Arctic Ocean, as was the Hg burial rate into the sediment.
Using samples collected during the German GEOTRACES TransArcII (GN04) and the U.S. Arctic GEOTRACES (GN01) cruises in August−October 2015, authors estimated the particulate mercury (Hgp) export flux in the central Arctic Ocean and the outer shelf. These new data allowed them to i) calculate Hgp normalized to suspended particulate matter and partition coefficient for the Arctic Ocean; ii) use Hgp and 234Th observations to estimate the Hgp export flux based on the 234Th/238U disequilibrium and iii) re-estimate the net Hg burial rates from Arctic sediment cores.
This comprehensive study of the Arctic particulate Hg behaviour led to the estimate of 156 Mg year−1 Hgp export from the surface ocean and 28 Mg year−1 Hg burial rate, fluxes extrapolated to the entire Arctic Ocean, including the inner shelf.
Reference:
Tesán Onrubia, J. A., Petrova, M. V., Puigcorbé, V., Black, E. E., Valk, O., Dufour, A., Hamelin, B., Buesseler, K., Masqué, P., Le Moigne, F. A. C., Sonke, J. E., Rutgers van der Loeff, M. Heimbürger-Boavida, L.-E. (2020). Mercury Export Flux in the Arctic Ocean Estimated from 234 Th/ 238 U Disequilibria. ACS Earth and Space Chemistry, acsearthspacechem.0c00055. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsearthspacechem.0c00055
