Anthropogenic aerosol has become a dominant source of zinc in the deep water of the Northern South China Sea
Liao and his colleagues (2021, see reference below) determined zinc (Zn) concentrations and isotope compositions (66δZn) in sinking particles collected at 2000 and 3500 m at the SEATS station of the Northern South China Sea (NSCS) from April 2014 to March 2015. This time series allowed them to disentangle the contribution of different Zn sources to the deep ocean in this area. Their data revealed that anthropogenic aerosol Zn accounted for 64 ± 10% of the total Zn in sinking particles for more than 50% of the sampling period, indicating that anthropogenic aerosol Zn has become a dominant form of Zn source in the deep water. When the productivity is high, an elevated contribution of the biogenic hard parts or scavenging Zn on organic materials is detected.
Contrastingly, during the low flux period, authigenic particle signatures are also found.
Applying new values for the solubility and fluxes of aerosol Zn in the ocean, the authors found that the Zn flux has been significantly underestimated in previous studies. The updated global aerosol Zn input to the ocean, ranging from 0.3 to 3.0 Gmol yr_1, is comparable to the output magnitude from hydrothermal and riverine sources. The updated Zn residence time would then be down to 1400 years on average.
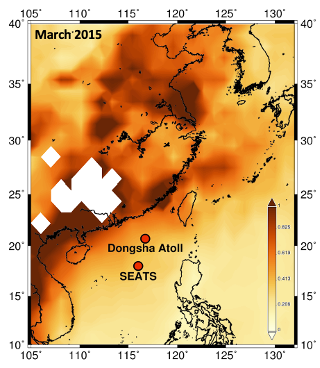
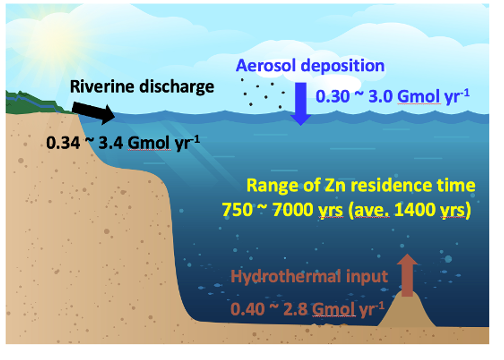
Figure: (Left) The aerosol optical depth from satellite exhibits high anthropogenic aerosol transport from East Asia to the Northwestern Pacific Ocean and its marginal seas during spring season. Anthropogenic aerosols contain highly enriched, highly soluble, and isotopically light trace metals, e.g., Zn. (Right) We found that anthropogenic aerosols are the major Zn source in the sinking particles collected at SEATS, Taiwan’s time series station in the South China Sea. Our study suggests that aerosols are one of the major Zn sources to the global ocean.
Reference:
Liao, W.-H., Takano, S., Tian, H.-A., Chen, H.-Y., Sohrin, Y., & Ho, T.-Y. (2021). Zn elemental and isotopic features in sinking particles of the South China Sea: Implications for its sources and sinks. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 314, 68–84. Access the paper: 10.1016/j.gca.2021.09.013
