A new application of aerosol iron isotopes: tracing anthropogenic iron; an example of the North Atlantic Ocean
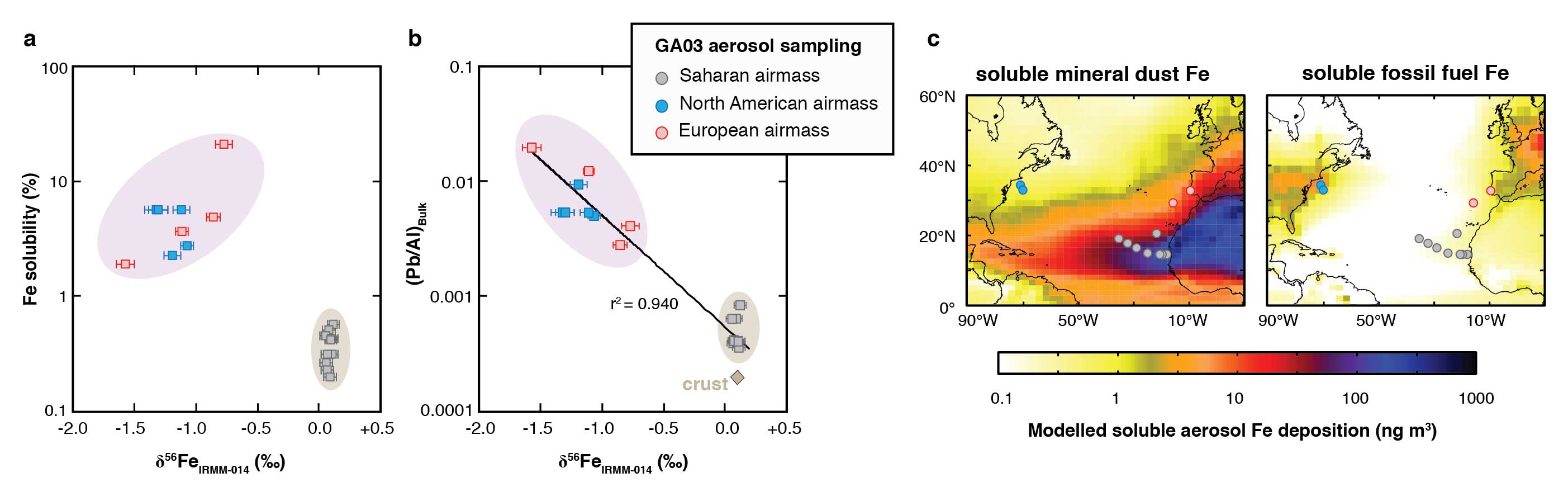
Conway and co-authors (2019, see reference below) present the first evidence that anthropogenic iron (Fe) from combustion sources is visible at the basin scale, using iron isotopic composition (δ56Fe) analysis of the soluble aerosol phases collected during GEOTRACES cruise GA03 in the North Atlantic Ocean. Off Sahara, soluble aerosol samples have near-crustal δ56Fe whereas those from near North America and Europe display δ56Fe values as light as −1.6‰. Coupled to aerosol deposition modeling these results reveal that soluble anthropogenic aerosol Fe flux to the global surface oceans is highly likely to be underestimated.
Reference:
Conway, T. M., Hamilton, D. S., Shelley, R. U., Aguilar-Islas, A. M., Landing, W. M., Mahowald, N. M., & John, S. G. (2019). Tracing and constraining anthropogenic aerosol iron fluxes to the North Atlantic Ocean using iron isotopes. Nature Communications, 10(1), 2628. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-10457-w
