Multiple controls on the dissolved aluminium fate in the Western Atlantic Ocean
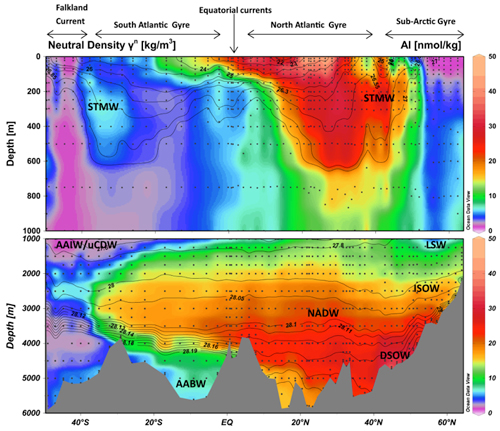
Thanks to the most impressive set of dissolved aluminium (Al) and silicon (Si) data ever published in the Atlantic Ocean, Middag and co-workers (2015, see reference below) are thoroughly scanning the processes determining their oceanic distribution. They reveal that i) atmospheric inputs are affecting only the surface and subsurface waters, ii) there is an elusive but obvious coupling between Si-containing biogenic particles and Al, iii) scavenging is occurring faster than the horizontal advective transports preventing the use of Al as quantitative water mass tracer, and iv) not observed at a basin-wide scale before, suspended sediments are a significant source for dissolved Al in the deep waters.
Reference:
Middag, R., van Hulten, M. M. P., Van Aken, H. M., Rijkenberg, M. J. A., Gerringa, L. J. A., Laan, P., & de Baar, H. J. W. (2015). Dissolved aluminium in the ocean conveyor of the West Atlantic Ocean: Effects of the biological cycle, scavenging, sediment resuspension and hydrography. Marine Chemistry. doi:10.1016/j.marchem.2015.02.015 Click here to download the paper.
