Conservative behavior of radiogenic neodymium isotopes in the South Pacific interior
Radiogenic neodymium isotopes (εNd) are widely used to trace ocean circulation, yet their application relies on the assumption that εNd behaves conservatively away from ocean margins. Whether this assumption holds in the slowly ventilated South Pacific, a basin characterized by widespread volcanic provinces and extensive abyssal plains, has remained debated.
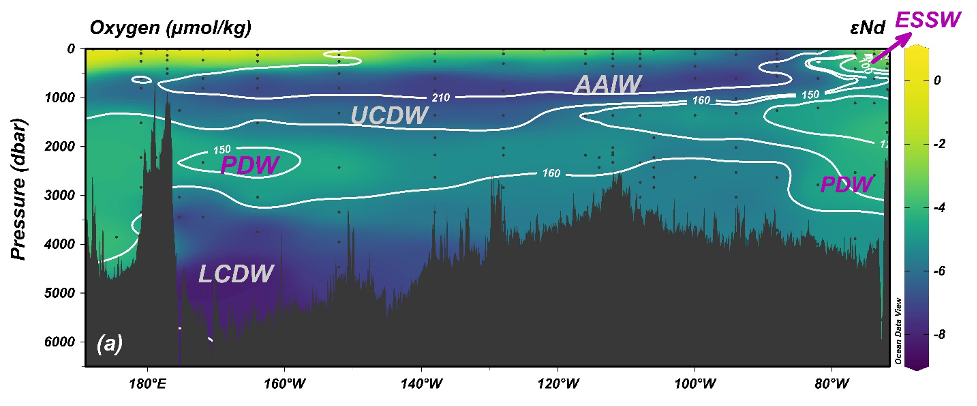
Zhang and co-workers (2026, see reference below) present full-depth measurements of εNd and Nd concentrations along the GEOTRACES GP21 zonal transect (26–32°S) across the South Pacific basin (Figure 1). Surface seawater εNd values show pronounced and systematic variability, revealing a clear volcanic imprint in the western South Pacific Gyre following the explosive January 2022 eruption of the Hunga Tonga–Hunga Ha’apai (HTHH) volcano (2024, read science highlight here). However, using an Optimum Multi-Parameter Analysis (OMPA), the authors demonstrate that both εNd and Nd concentrations in intermediate and deep waters behave largely conservatively across the oligotrophic South Pacific Gyre, with deviations primarily confined to the eastern and western boundaries. The influence of the volcanic eruption appears to be largely limited to surface waters.
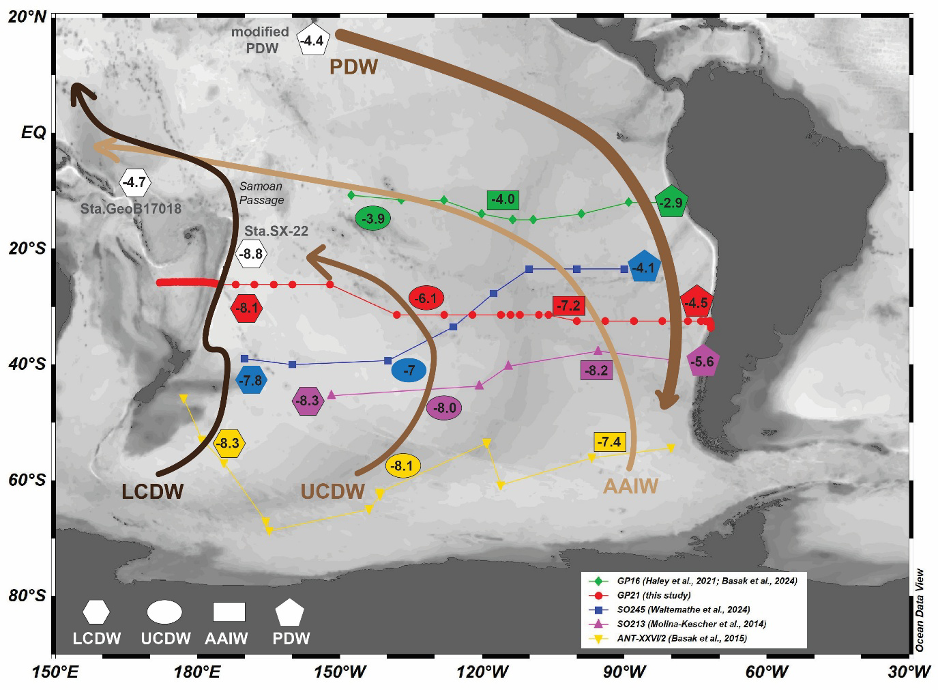
By synthesizing GP21 with other cross-Pacific zonal sections in the South Pacific, the study further shows that conservative εNd behavior persists from subpolar to subtropical latitudes. Notably, Lower Circumpolar Deep Water (LCDW) exhibits no significant isotopic modification during its northward transport from the subpolar South Pacific to approximately 20°S, indicating a negligible influence from benthic Nd inputs along its advective pathway (Figure 2). Together, these findings provide strong observational support for the use of εNd as a robust tracer of water mass mixing in the central South Pacific away from ocean margins.
Reference:
Zhang, Z., Xu, A., Chen, X., Hathorne, E., Gutjahr, M., Frank, M., 2026. Conservative behavior of radiogenic neodymium isotopes in the South Pacific interior. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 678, 119850. Access the paper: 10.1016/j.epsl.2026.119850
Zhang, Z., Xu, A., Hathorne, E., Gutjahr, M., Browning, T.J., Gosnell, K.J., Liu, T., Steiner, Z., Kiko, R., Yuan, Z., Liu, H., Achterberg, E.P., Frank, M., 2024. Substantial trace metal input from the 2022 Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai eruption into the South Pacific. Nat. Commun. 15, 8986. Access the paper: 10.1038/s41467-024-52904-3
