Contrasting organic carbon remineralisation rates revealed by particulate excess barium in the North Pacific and South China Sea
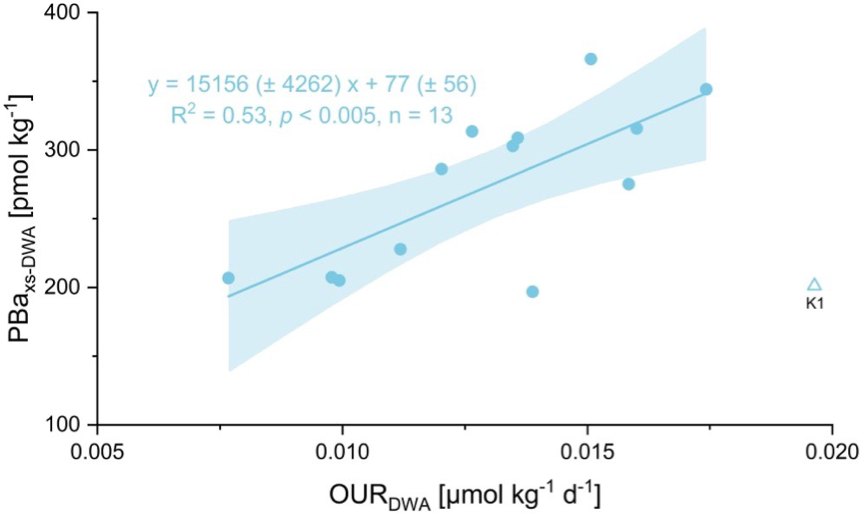
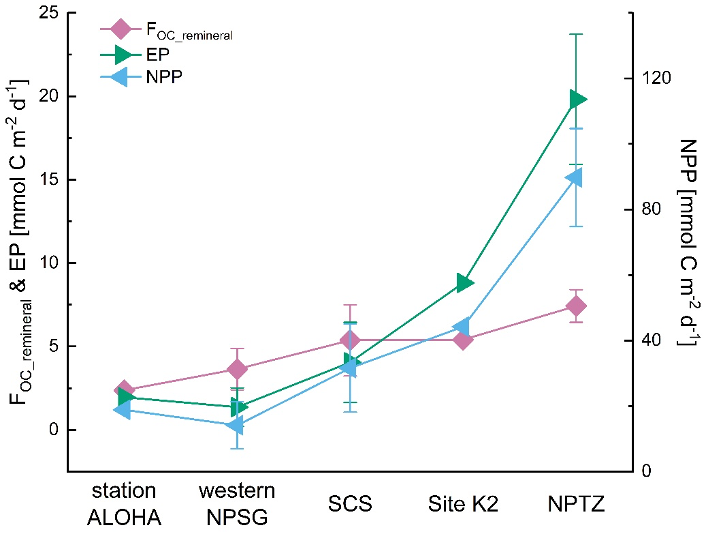
Yuan and co-workers (2025, see reference below) quantify organic carbon (OC) remineralisation in the twilight zone (150-600 m) of the western North Pacific and the South China Sea (SCS) using particulate excess barium (PBaxs) as a proxy. By developing a new PBaxs-oxygen utilisation rate transfer function, the study constrains twilight zone OC remineralisation fluxes (FOC_remineral) and reveals pronounced spatial heterogeneity across the study area. The dataset, acquired from multiple cruises including three GEOTRACES cruises (GP09, GPpr15 summer, and GPpr15 winter) shows substantially higher FOC_remineral in the nutrient-rich North Pacific Transition Zone (NPTZ) than in the oligotrophic western North Pacific Subtropical Gyre (NPSG) and SCS. FOC_remineral patterns also closely follow satellite-derived net primary production (NPP) and export production (EP), and higher euphotic zone biological pump carbon export efficiency (e‐ratio) coupled with lower twilight zone OC remineralisation ratio (r‐ratio) in the NPTZ indicates enhanced carbon sequestration potential relative to the NPSG and SCS. Overall, these results demonstrate the utility of PBaxs as a proxy for twilight zone OC remineralisation and provide a framework for assessing cross-regional variability in the biological pump.
Reference:
Yuan, Y., Zhao, S., Lin, W., Li, Y., Yu, J., Huang, Y., et al. (2025). Quantifying organic carbon remineralization in the twilight zone of the western North Pacific using particulate excess barium. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 39, e2025GB008755.
Access the paper: 10.1029/2025GB008755
