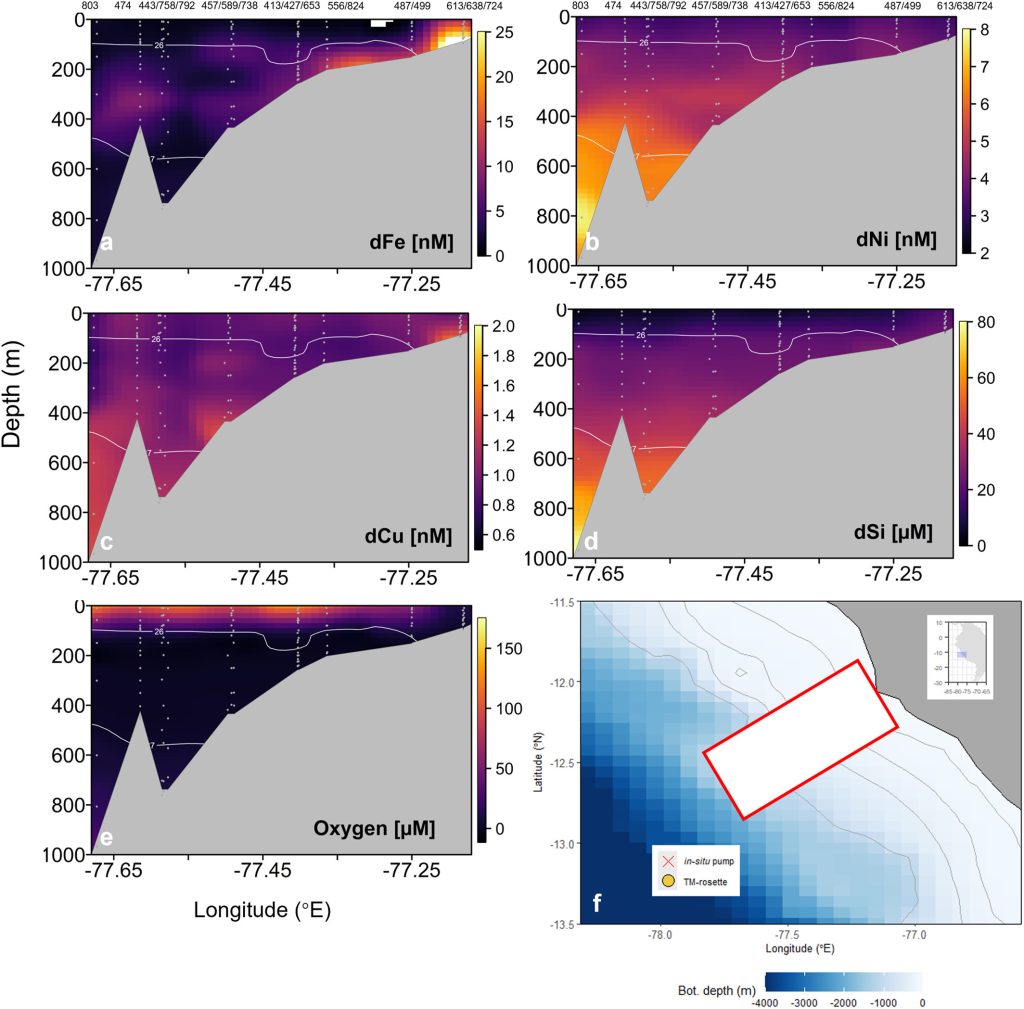
Trace metal effluxes from Peruvian shelf sediments
Shelf sediments are a major reservoir of labile trace metals. For dissolved redox sensitive elements such as iron (Fe), shelf sediments underneath oxygen minimum zones are typically a major source to the water column. However, quantifying the associated dissolved fluxes is methodologically challenging. Liu and colleagues (2025, see reference below), compare four different methods for estimating the Fe flux from Peruvian shelf sediments and show that the results are quite variable. Estimates of benthic Fe release suggest Fe residence times in the water column from 5 days to 7 years for the Peruvian shelf depending on exactly what spatial scale the benthic efflux is constrained over. This largely reflects the strong attenuation of dissolved Fe efflux from shelf sediments on spatial scales of 0.1-10 m from the seafloor.
Reference:
Liu, T., Plass, A., Gledhill, M., Scholz, F., Achterberg, E. P., & Hopwood, M. J. (2025). Trace Metal Effluxes From Peruvian Shelf Sediments Constrained in Parallel by Benthic Lander Mounted Pumps and Pelagic Rosette Sampling. Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences, 130. Access the paper: 10.1029/2024jg008583
