Distribution and fate of the lithogenic and anthropogenic aerosols over the Mediterranean and Black Seas
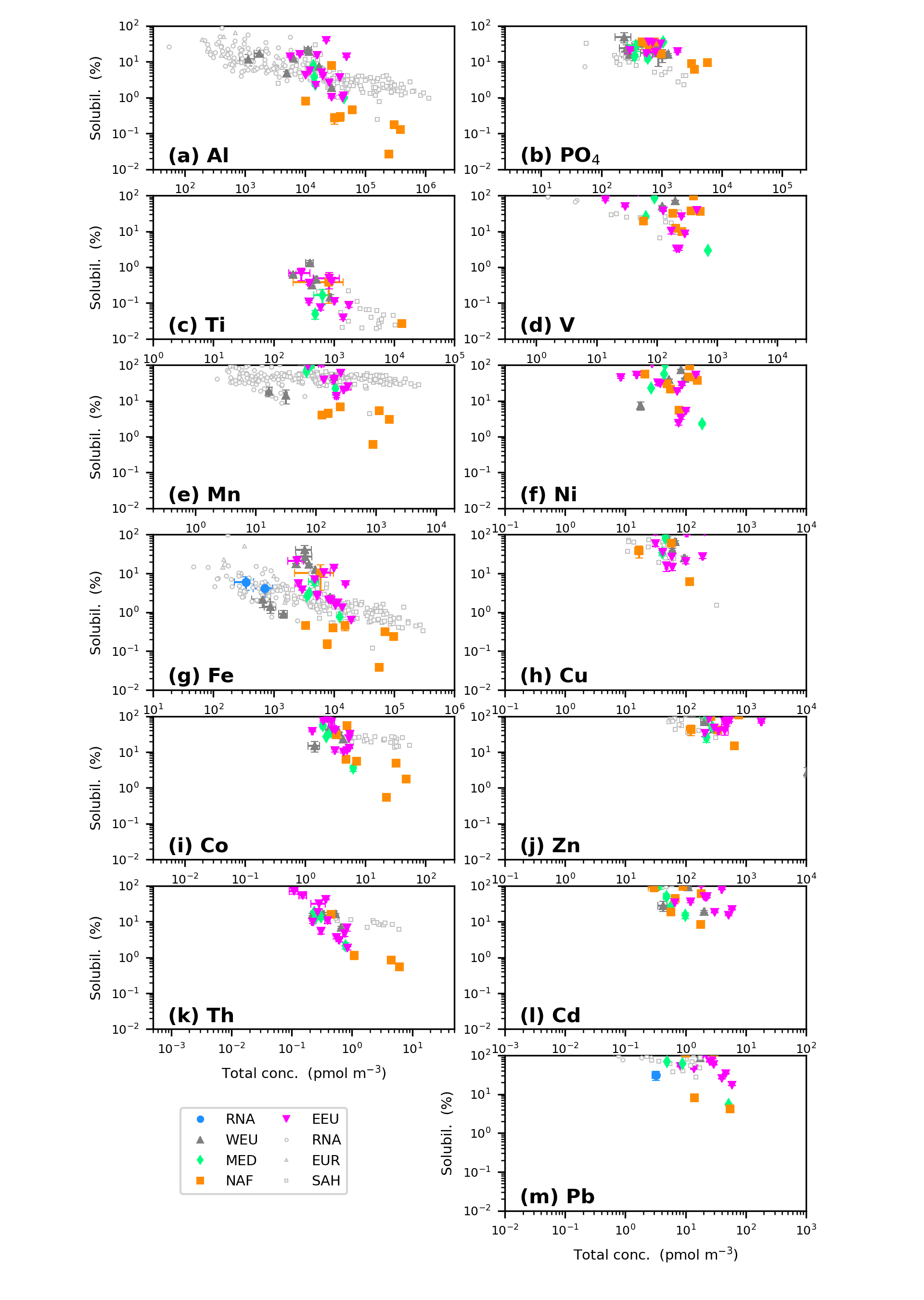
Thanks to aerosols samples collected in summer 2013, Shelley and co-authors (2024, see reference below) propose an extensive coverage of the distribution and fate of the lithogenic and anthropogenic aerosols over the Mediterranean and Black Seas (GEOTRACES cruise GA04). They confirm that the trace element sources are both lithogenic mineral dust and various anthropogenic emissions for these intra-continental seas, including shipping activities. Fractional solubilities of the lithogenic elements* vary considerably with atmospheric dust load, having lower solubility in dusty aerosols and often higher solubility in polluted European air masses. Contrastingly, the anthropogenic elements** from these air masses are highly soluble. Comparison with the fate of the same elements over the Atlantic Ocean is discussed. The decreasing west-east nitrogen/phosphorus (N/P) gradient in the dry deposition flux could contribute to the P-limited status of the eastern basin.
*Lithogenic elements: aluminium (Al), titanium (Ti), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), cobalt (Co) and thorium (Th).
**Anthropogenic elements: phosphorus (P), vanadium (V), nickel (Ni), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), cadmium (Cd) and lead (Pb).
3).
Reference:
Shelley, R. U., Baker, A. R., Thomas, M., & Murphy, S. (2024). Aerosol trace element solubility and deposition fluxes over the Mediterranean and Black Sea basins. Access the paper: 10.5194/egusphere-2024-2667
Jickells, T. D., Baker, A. R., and Chance, R. (2016). Atmospheric transport of trace elements and nutrients to the oceans, 515 Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series A-Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences, 374, 20150286. Access the paper: 10.1098/rsta.2015.0286
