Upwelled hydrothermal iron stimulates massive phytoplankton blooms in the Southern Ocean
Joint Science Highlight with US-Ocean Carbon & Biogeochemistry (US-OCB).
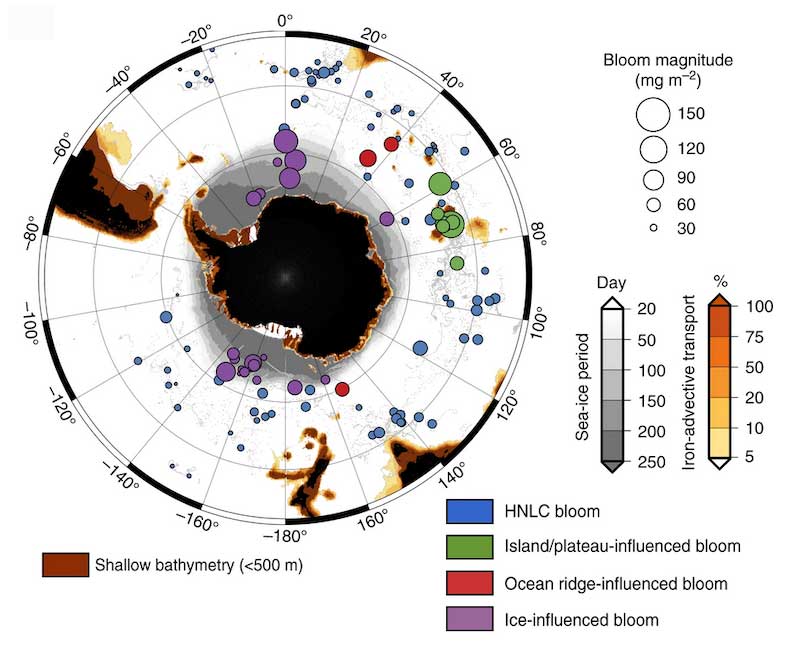
In a recent study, Ardyna et al (2019, see reference below) combined observations of profiling floats with historical trace element data and satellite altimetry and ocean color data from the Southern Ocean to reveal that dissolved iron (Fe) of hydrothermal origin can be upwelled to the surface. Furthermore, the activity of deep hydrothermal sources can influence upper ocean biogeochemical cycles of the Southern Ocean, and in particular stimulate the biological carbon pump.
Reference:
Ardyna, M., Lacour, L., Sergi, S., d’Ovidio, F., Sallée, J.-B., Rembauville, M., Blain, S., Tagliabue, A., Schlitzer, R., Jeandel, C., Arrigo, K.R., Claustre, H. (2019). Hydrothermal vents trigger massive phytoplankton blooms in the Southern Ocean. Nature Communications, 10(1), 2451. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09973-6
