What drives the silicon budget in the Bay of Bengal? The isotope composition clues…
The first data set of dissolved silicon isotope composition (δ30Si) along with concentrations (DSi) in seawater of the northern Indian Ocean is presented from the Bay of Bengal (BoB) region.
Elevated Si (>3 µmol/kg) in surface waters of coastal stations indicates the continental supply, whereas a spike of Si (~30 µmol/kg) and a salinity maxima at depth 60 m of the southernmost station hint at intrusion of the Arabian Sea High Salinity waters. In the central bay, higher δ30Si in surface waters indicates greater utilisation of the available Si via diatom production. DSi and δ30Si in surface waters of the BoB vary dramatically in response to the Si supply and its consumption through biological production.
Modelling δ30Si in the deep/bottom waters of the BoB hints at dissolution of diatoms rather than lithogenic clays at/near the sediment–water interface as the main cause of the elevated Si concentrations in the bay.
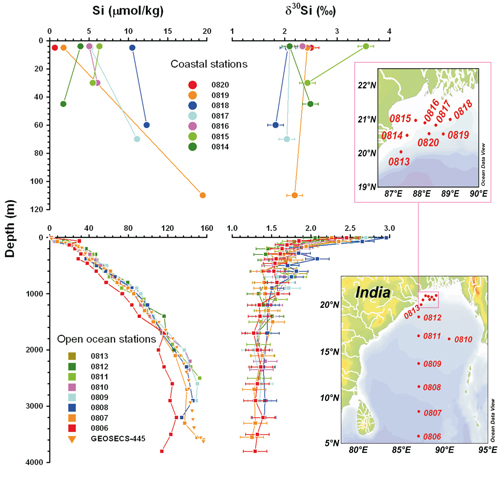
Figure. Depth profiles of dissolved Si concentrations (left panel) and δ30Si (right panel) are shown for the coastal stations 0814–0820 (upper panel) and open ocean stations 0806–0813 (lower panel). Locations of coastal and open ocean stations are also given. Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Singh, S.P., Singh, S.K., Bhushan, R., Rai, V.K., 2015. Dissolved silicon and its isotopes in the water column of the Bay of Bengal: Internal cycling versus lateral transport. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 151, 172-191. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2014.12.019. Click here to access the paper.
