Trace metal fluxes of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc from the Congo River into the South Atlantic Ocean are supplemented by atmospheric inputs
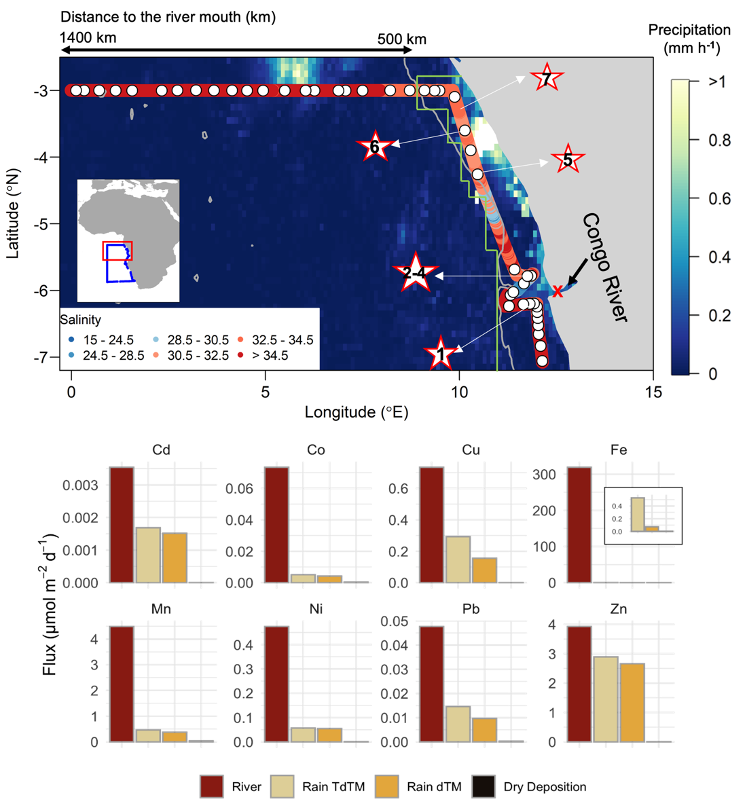
The Congo River, as the second largest river globally, supplies vast amounts of trace metals (TMs) to the South Atlantic via a far extended freshwater plume. However, existing work suggests a discrepancy within the TM budgets in the Congo plume and points to unknown source other than the Congo River or shelf sediments. Considering high precipitation rates of >200 mm across the Congo shelf during October to December, in a global context, coincident with the timing of GEOTRACES cruise GA08, Liu and colleagues (2023, see reference below) show that wet deposition (rainfall) augments some fluxes of TMs from the Congo River. Specifically, wet deposition contributed the equivalent of 43% dissolved cadmium, 21% dissolved copper, 20% dissolved lead and 68% dissolved zinc of the Congo River fluxes. This finding demonstrates an important role of wet deposition in contributing TMs to such a major river plume and to the open ocean.
Reference:
Liu, T., Hopwood, M. J., Krisch, S.,Vieira, L. H., & Achterberg, E. P. (2023). Trace metal fluxes of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn from the Congo River into the South Atlantic Ocean are supplemented by atmospheric inputs. Geophysical Research Letters, 50, e2023GL107150. Access the paper: https://doi.org/10.1029/2023GL107150
