New trace metal data in the Seas of Japan and Okhotsk
Yuzuru Nakaguchi and his colleagues (2022, see references below) realized full-depth and section distributions of the dissolved (d), total dissolvable (td), and labile particulate (lp) phases of Al, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb in seawater samples collected from the Seas of Japan and Okhotsk during the GEOTRACES-Japan program. This allowed these authors to establish that:
- Although high lpM/tdM ratios suggest active scavenging in the Seas of Japan and Okhotsk, the distributions of trace metals in seawater are distinct between the two seas, reflecting an interplay between the circulation (advection of deep waters from the Pacific Ocean) and margin inputs.
- In the surface waters of the Sea of Japan, enrichment factor (EF) values of dMn, dCo, dNi, dCu, dZn, dCd, and dPb range within 103–106, implying that these elements are supplied from anthropogenic sources via the atmosphere. In the Sea of Okhotsk, the concentrations of dAl, lpAl, dMn, lpMn, dFe, lpFe, dCo, and lpCo were high owing to supply from continental sources via the Amur River and atmosphere, although less contaminated than in the Sea of Japan.
- However, trace metal enrichments due to margin inputs and the lateral transport of Mn, Fe, and Co by the Okhotsk Sea intermediate water (OSIW) can be an important source for the North Pacific Intermediate Waters (NPIW).
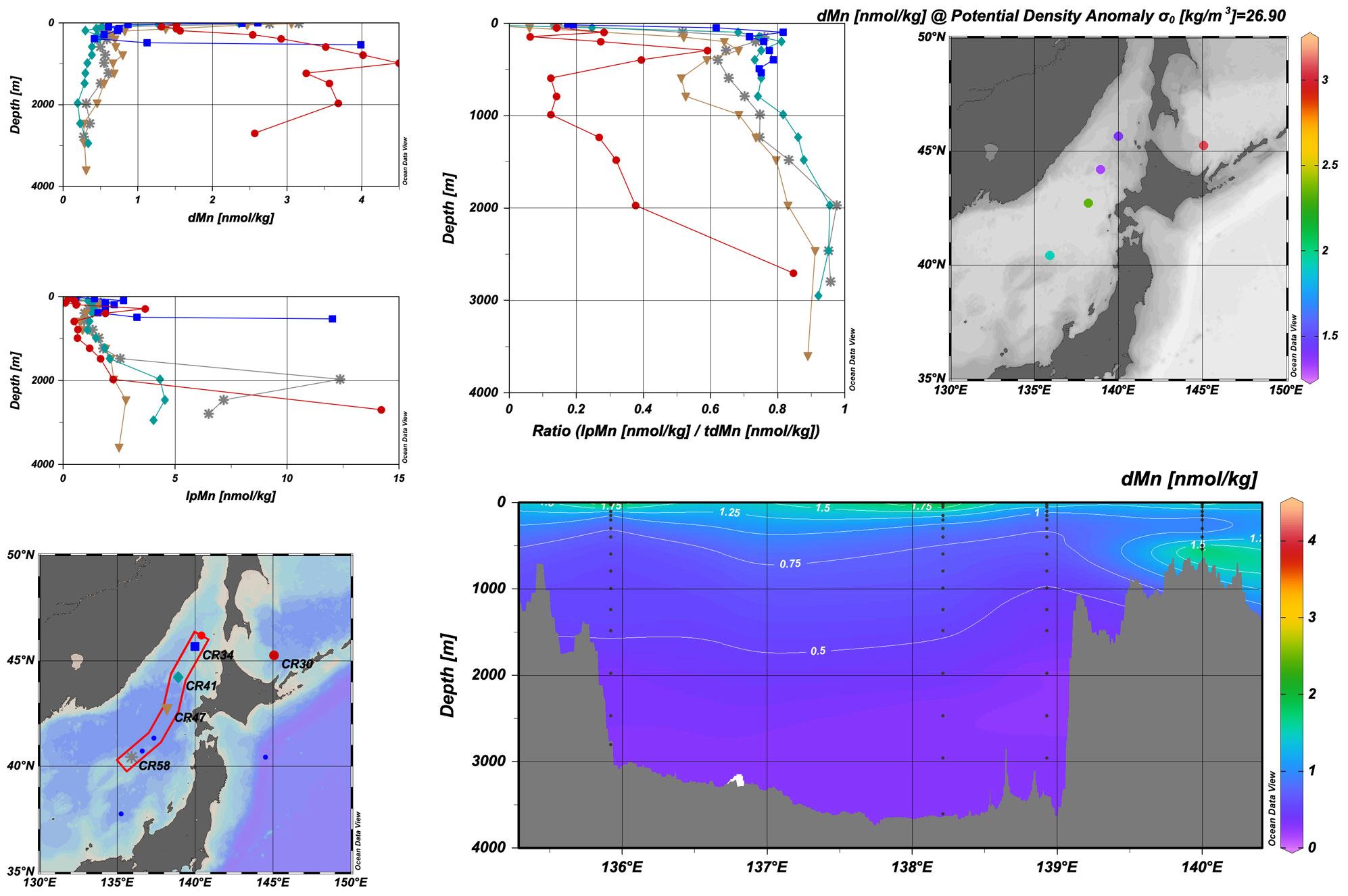
Figure: Distribution of dissolved Mn (dMn), labile particulate Mn (lpMn), and the lpMn/total dissolvable Mn (tdMn) ratio in the Seas of Japan and Okhotsk. In the Japan Sea, dMn is high in surface water and low in deep water (> 1000 m depth), where lpMn accounts for >70% of tdMn. In contrast, dMn has a maximum at intermediate depths in the Okhotsk Sea. dMn and lpMn around σ0 = 26.9 are entrained into the Okhotsk Sea intermediate water (OSIW).
Reference:
Nakaguchi, Y., Sakamoto, A., Asatani, T., Minami, T., Shitashima, K., Zheng, L., & Sohrin, Y. (2022). Distribution and stoichiometry of Al, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, Cd, and Pb in the Seas of Japan and Okhotsk. Marine Chemistry, 241, 104108. Access the paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marchem.2022.104108
