Lead isotopes, reversible scavenging and ventilation processes in the South Atlantic Ocean
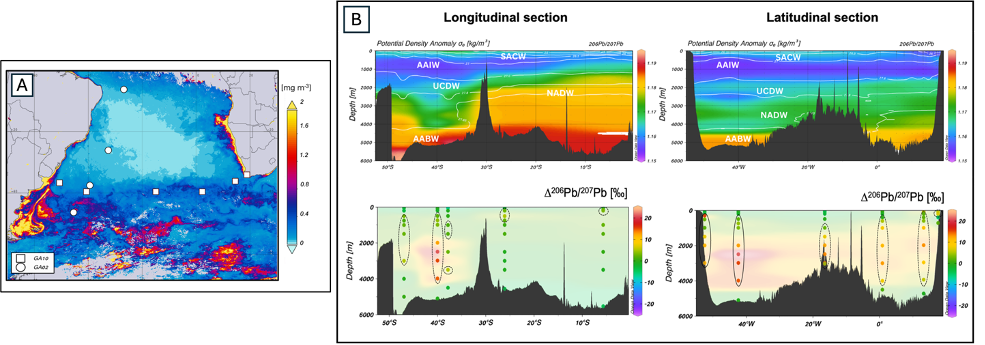
Olivelli and co-authors (see reference below) present seawater lead concentrations and lead isotopes for 10 depth profiles collected in the South Atlantic Ocean as part of the GA02 and GA10 GEOTRACES cruises. Using an extended optimum multiparameter (eOMP) analysis, allowing them to deconvolute the horizontal (advected) from the vertical (scavenged) lead transport, they 1) confirm that anthropogenic lead is transported to the deepest part of the ocean by reversible scavenging, 2) show that this reversible scavenging is intensified in areas characterised by high particle loads as for example the Brazil-Malvinas confluence area, and 3) warn us to use isotope lead ratios to trace water mass movements and/or ocean ventilation in areas rich in particles, where reversible scavenging is expected to be strong.
Reference:
Olivelli, A., Paul, M., Xu, H., Kreissig, K., Coles, B. J., Moore, R. E. T., Bridgestock, L., Rijkenberg, M., Middag, R., Lohan, M. C., Weiss, D. J., Rehkämper, M., & van de Flierdt, T. (2024). Vertical transport of anthropogenic lead by reversible scavenging in the South Atlantic Ocean. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 646, 118980. Access the paper: 10.1016/j.epsl.2024.118980
