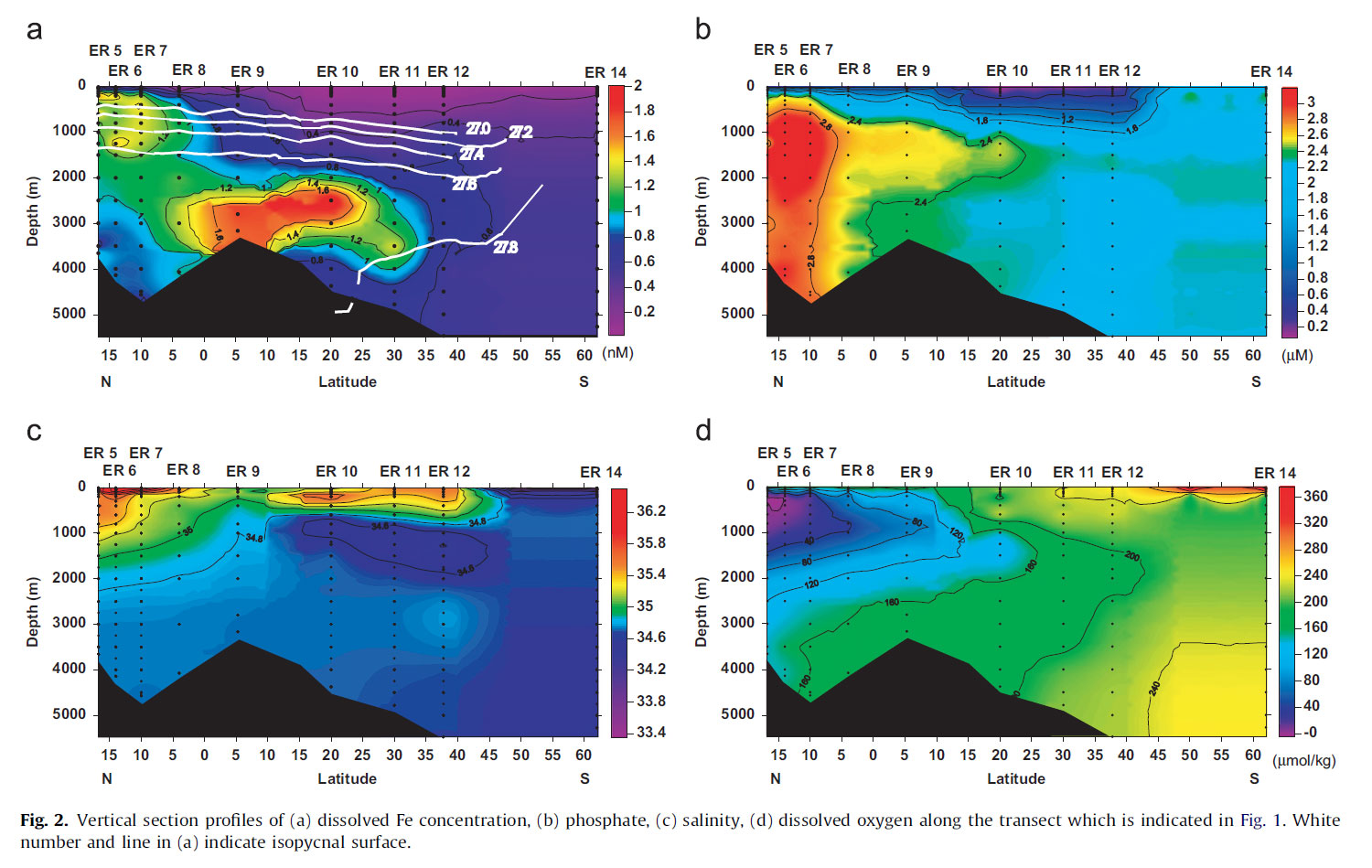
Hydrothermalism: A significant dissolved iron source for the deep waters ?
A North-South basin-scale full-depth section profile of dissolved Fe was realized in the Indian Ocean, as part of the first GEOTRACES Japanese cruise (Nov 2009 – Jan 2010). The data clearly show that hydrothermal Fe is distributed over 3000 km distance around a depth of ~ 3000 m, and that a large fraction of this Fe is truly dissolved. Several other sources supplying dissolved Fe to deep waters (e.g terrestrial Fe input) with a persistent condition in the oxygen minimum zone (OMZ) were also evidenced.
Source: Science Direct (click on the image to view it larger)
Reference:
Jun Nishioka, Hajime Obata, Daisuke Tsumune (2013), Evidence of an extensive spread of hydrothermal dissolved iron in the Indian Ocean : Earth and Planetary Science Letters, ELSEVIER (361) p. 26-33, DOI: /10.1016/j.epsl.2012.11.040