Dissolved zinc and silicate decoupling in the North Pacific Ocean
Large-scale distributions of dissolved zinc (Zn) in the western and central subarctic North Pacific Ocean was established as part of the North Pacific GEOTRACES section GP02. Kim and co-workers could figure out interesting Zn behavior in this area:
- Decoupling between Zn and Silicate in the intermediate water,
- Zn* values (used to show the variability in the relationship between dissolved Zn and silicate in the ocean) are strongly positive in the intermediate waters of the western and central subarctic North Pacific,
- Dissolved Zn and soluble reactive phosphorus (SRP) concentrations were relatively high in the intermediate water.
The authors suggest that these particular values observed in the intermediate waters of the subarctic North Pacific result of remineralization from Zn-rich biogenic particles, weak reversible scavenging onto sinking biogenic particles, and sedimentary Zn sources.
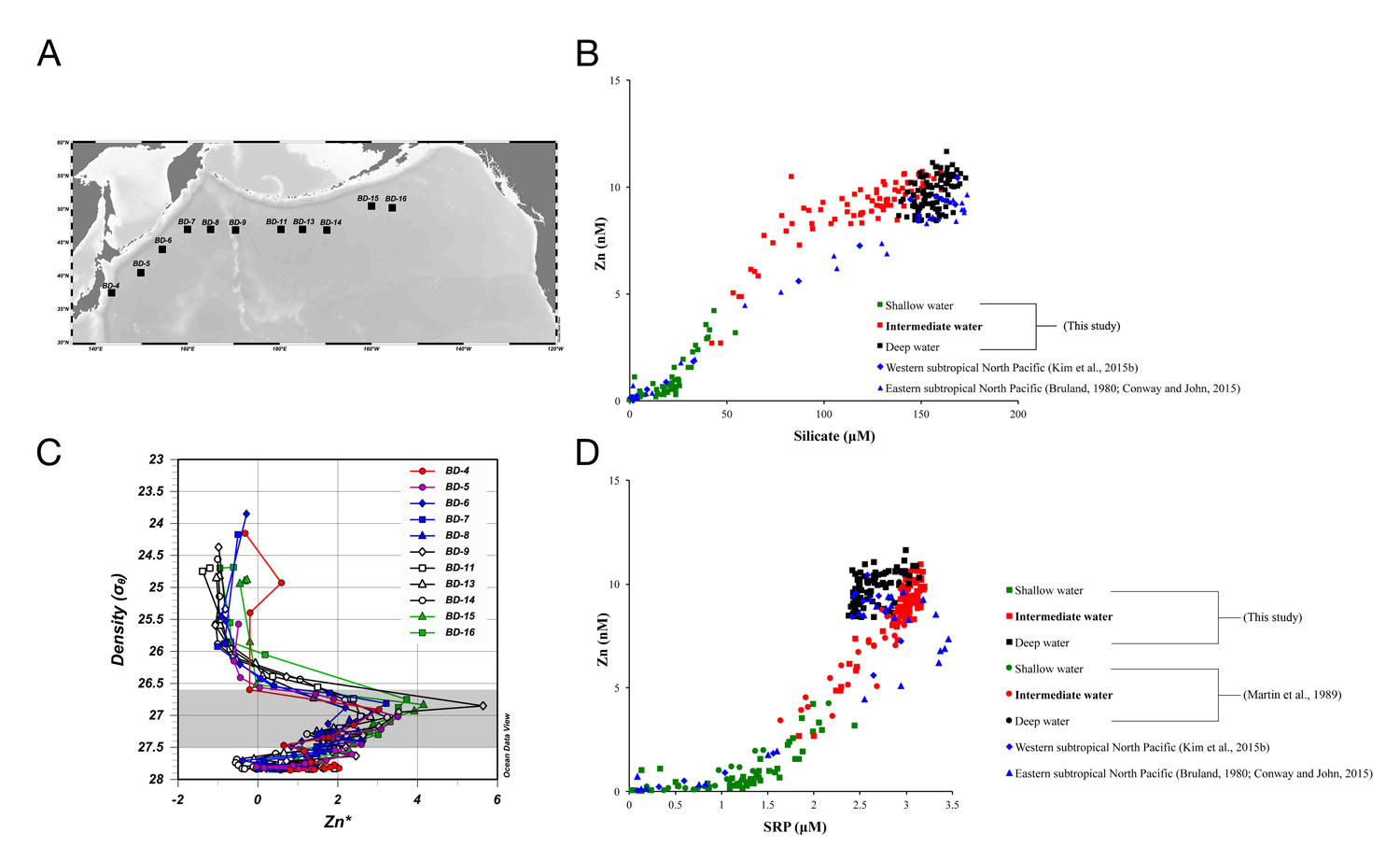 Figure: (A) Locations of sampling stations in the subarctic North Pacific. (B) Relationships between dissolved Zn and silicate. (C) Zn* as a function of density. The shaded bar represents density range of the intermediate water (26.6–27.5 σθ). (D) Relationships between dissolved Zn and SRP. In (B) and (D), green, red, and black indicate shallow water, intermediate water, and deep water in the subarctic North Pacific, respectively, while blue indicates data from the subtropical North Pacific. Click here to view the figure larger.
Figure: (A) Locations of sampling stations in the subarctic North Pacific. (B) Relationships between dissolved Zn and silicate. (C) Zn* as a function of density. The shaded bar represents density range of the intermediate water (26.6–27.5 σθ). (D) Relationships between dissolved Zn and SRP. In (B) and (D), green, red, and black indicate shallow water, intermediate water, and deep water in the subarctic North Pacific, respectively, while blue indicates data from the subtropical North Pacific. Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Kim, T., Obata, H., Nishioka, J., & Gamo, T. (2017). Distribution of Dissolved Zinc in the Western and Central Subarctic North Pacific. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 31(9), 1454–1468. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GB005711
