When atmospheric dynamic controls the nutrient distributions in the ocean
Rainfall detection with satellites together with high-resolution data (~0.3°) for dissolved iron (DFe), aluminium (DAl), and inorganic phosphorus (DIP), confirm the existence of a sharp north–south biogeochemical boundary in the surface nutrient concentrations of the (sub)tropical Atlantic Ocean.
Wet deposition in the region of the intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ) acts as the major dissolved iron (DFe) source to surface waters. These variations of higher Fe inputs tied to the ITCZ movements drive a shift in the latitudinal distribution of N2 fixation and subsequent phosphate depletion in surface waters.
Thus, atmospheric dynamic is driving surface nutrient concentrations and microbial (diazotrophic) activity, which divide the (sub)tropical Atlantic into a high-phosphate, low-iron system in the south, and a low-phosphate, high-iron system in the north.
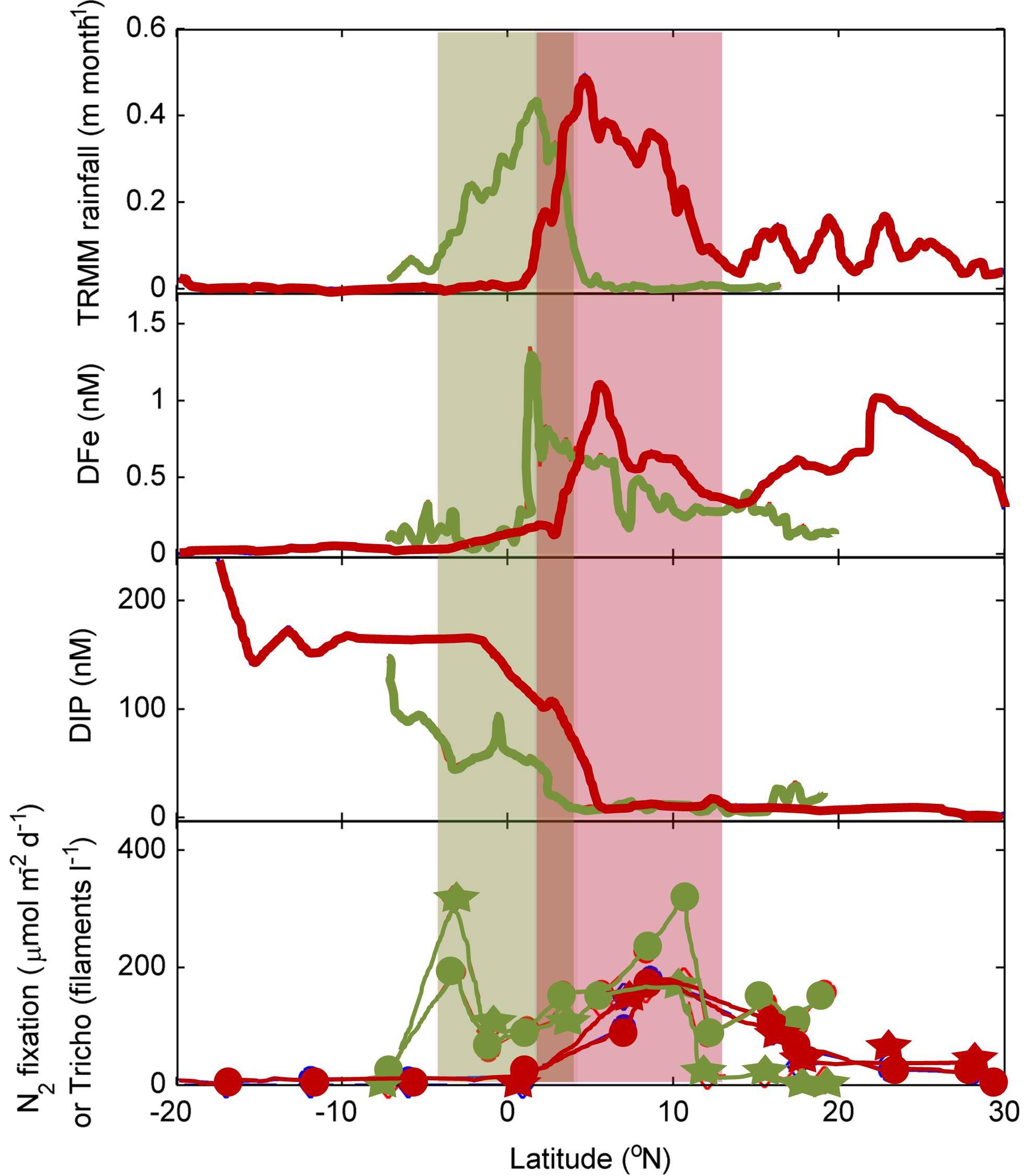
Figure: From the top to the bottom: Data from the AMT-17 (red) and D361 (green) cruises for satellite derived rainfall, surface DFe, surface DIP, and depth integrated N2 fixation (filled circles) and Trichodesmium spp. abundance (filled stars). Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Schlosser, C., Klar, J. K., Wake, B. D., Snow, J. T., Honey, D. J., Woodward, E. M. S., Lohan, M. C., Achterberg, E.D., Moore, C. M. (2014). Seasonal ITCZ migration dynamically controls the location of the (sub)tropical Atlantic biogeochemical divide. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 111(4), 1438–42. doi:10.1073/pnas.1318670111.
