Paradoxical influence of hydrothermal methylmercury on local ecosystems
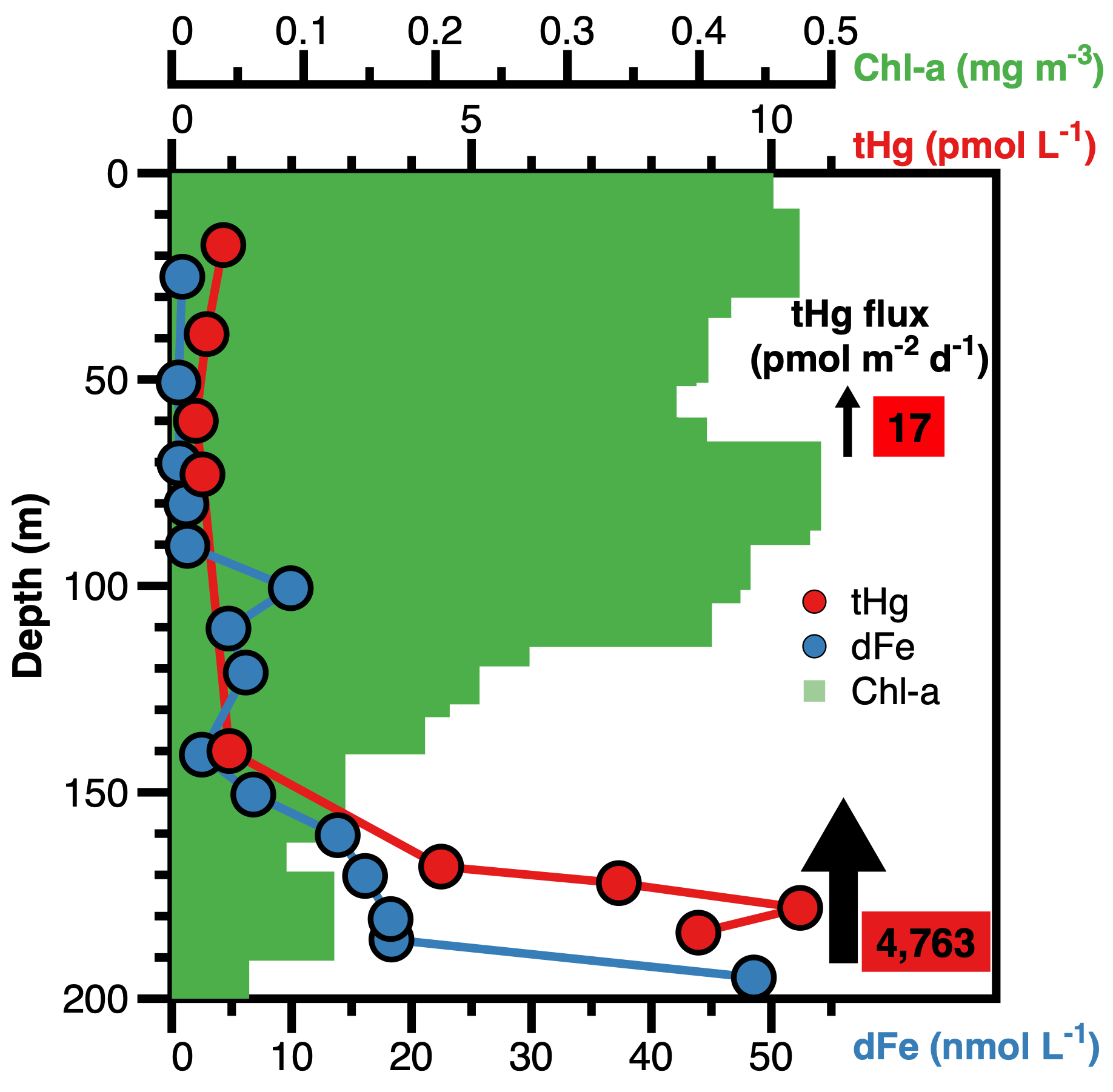
Torres Rodríguez and her colleagues (2025, see reference below) investigate hydrothermal mercury inputs at the Tonga volcanic arc and their impact on local surface ocean ecosystems. Although they identified high mercury fluxes (4,763 pmol m⁻² day⁻¹) reaching productive surface waters, they found that mercury concentrations in phytoplankton remain unexpectedly low. In fact, natural iron fertilisation from hydrothermal sources stimulates intense phytoplankton blooms, which dilute mercury at the cellular level and reduce the impact of hydrothermal mercury. The authors also provide a revised global estimate of hydrothermal mercury inputs, with a maximum of 120 t yr⁻¹—considerably lower than anthropogenic emissions.

Reference:
Torres-Rodriguez, N., Yuan, J., Dufour, A., Živković, I., Point, D., Boulart, C., Knoery, J., Horvat, M., Amouroux, D., Bonnet, S., Guieu, C., Sun, R., & Heimbürger-Boavida, L.-E. (2025). Natural Iron Fertilization Moderates Hydrothermal Mercury Inputs from Arc Volcanoes. Environmental Science &Amp; Technology, 59, 11039–11050. Access the paper:10.1021/acs.est.5c01767
