Where, how and which trace elements are released from dust at the sea surface?
Alex Baker and Tim Jickells (2017, see reference below) propose to answer to this question thanks to analysis of aerosols collected in the framework of the Atlantic Meridional Transect (AMT). They established the soluble concentrations of a range of trace metals (iron, aluminium, manganese, titanium, zinc, vanadium, nickel and copper) and major ions. They reveal much higher inputs to the North Atlantic Ocean compared to the South Atlantic Ocean, reflecting stronger land based emission sources in the Northern Hemisphere. Comparison of these inputs with the surface water contents of the same trace metals compiled in the GEOTRACES intermediate data product show surprising features that you will discover if you read this paper…
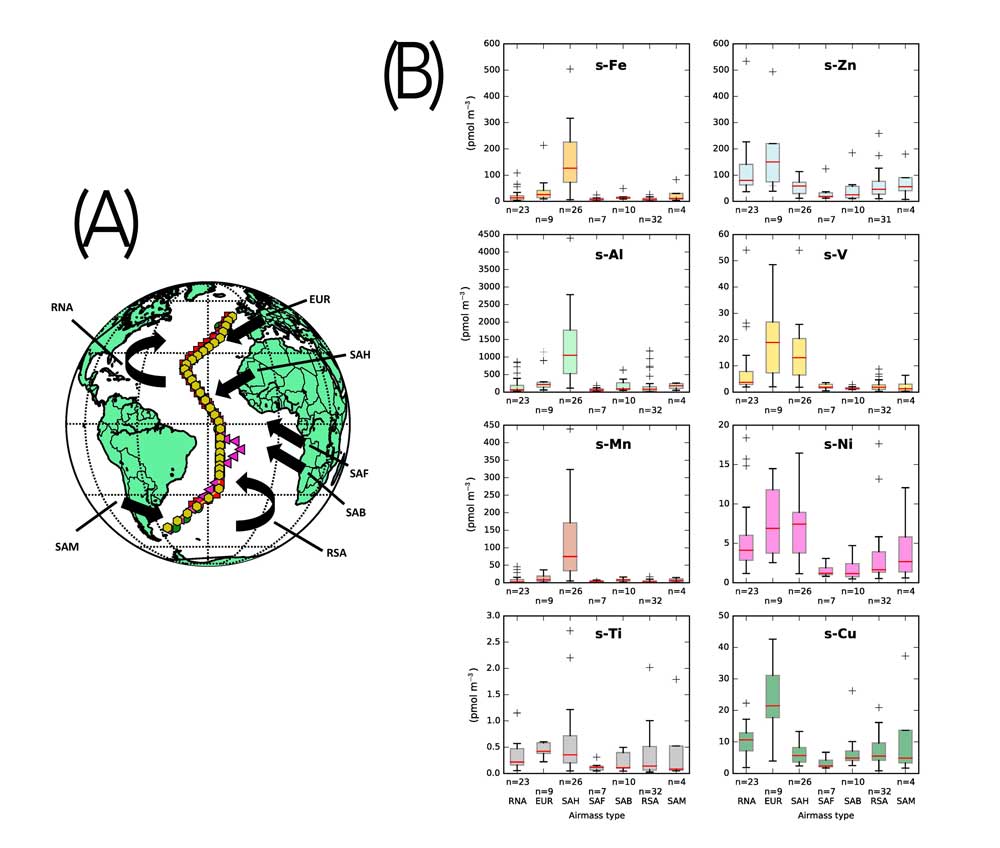 Figures: (A) Approximate tracks of the AMT cruises (dots and triangles) and general flow directions of the seven major atmospheric transport routes encountered during the cruises (arrows). Abbreviations for the air transport regimes are: continental Europe (EUR), North Africa including the Sahara and Sahel: (SAH), Southern Africa impacted by biomass burning emissions (SAB), Southern Africa not impacted by biomass burning (SAF), South America (SAM), remote North or South Atlantic i.e. not crossing land for at least 5 days prior to collection (RNA and RSA respectively). (B) Box and whisker plots showing the variations in the concentrations of iron, aluminium, manganese, titanium, zinc, vanadium, nickel and copper with air transport/source type for the AMT transect. They reveal much higher inputs to the North Atlantic Ocean, reflecting stronger land based emission sources in the Northern Hemisphere. Please click here to view the figure larger. (Figures modified from Progress in Oceanography)
Figures: (A) Approximate tracks of the AMT cruises (dots and triangles) and general flow directions of the seven major atmospheric transport routes encountered during the cruises (arrows). Abbreviations for the air transport regimes are: continental Europe (EUR), North Africa including the Sahara and Sahel: (SAH), Southern Africa impacted by biomass burning emissions (SAB), Southern Africa not impacted by biomass burning (SAF), South America (SAM), remote North or South Atlantic i.e. not crossing land for at least 5 days prior to collection (RNA and RSA respectively). (B) Box and whisker plots showing the variations in the concentrations of iron, aluminium, manganese, titanium, zinc, vanadium, nickel and copper with air transport/source type for the AMT transect. They reveal much higher inputs to the North Atlantic Ocean, reflecting stronger land based emission sources in the Northern Hemisphere. Please click here to view the figure larger. (Figures modified from Progress in Oceanography)
Reference:
Baker, A. R., & Jickells, T. D. (2017). Atmospheric deposition of soluble trace elements along the Atlantic Meridional Transect (AMT). Progress in Oceanography, 158, 41–51. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.pocean.2016.10.002
