Terrestrial iron inputs and reverse weathering in the Amazon mouth
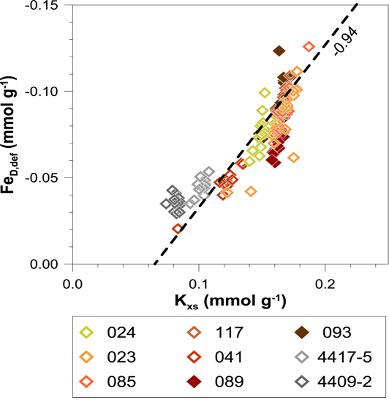
Understanding the key processes that condition the net input of chemical species to the ocean is an important challenge. Vosteen and his colleagues (2022, see reference below) applied sequential leaching to sediments from the Amazon shelf collected during the AMAZON-GEOTRACES process study (GApr11, cruise M147). They revealed that during early diagenesis, ∼22% of the Amazon River-derived iron (Fe) oxides are converted to Fe-containing clay minerals in Amazon shelf sediments. A clear correlation is observed between the deficiency of sedimentary Fe (FeD) on the Amazon shelf relative to river suspended sediment Fe (FeD, def) and the potassium (K) content of the sediments (Spiegel, 2021). The slope of the correlation corresponding to the Fe:K stoichiometry of authigenic clay minerals forming by reverse weathering on the Amazon shelf. However, mass balance calculations suggest that widely applied sequential extractions do not separate Fe-rich authigenic clay minerals from reactive Fe oxides and carbonates. The authors underline the importance of considering these land-ocean interface processes in the modelling of the oceanic Fe cycle.
Figures: (Left) Bathymetric map of the study area showing the location of sediment (red stars) and suspended particulate matter (black stars) samples along an offshore and an along shore transect. Water depth is shown as a colour scheme in steps of 20 m (0–100 m depth), 200 m (200–1,000 m depth) and 1,000 m (below 1,000 m depth).
(Right) Plot of FeD,def versus the sedimentary K uptake (Kxs) for all sediment samples. The individual stations are differentiated by colour. The slope of the dashed line corresponds to the Fe:K stoichiometry of authigenic clay minerals forming by reverse weathering on the Amazon shelf.
References:
Vosteen, P., Spiegel, T., Gledhill, M., Frank, M., Zabel, M., & Scholz, F. (2022). The Fate of Sedimentary Reactive Iron at the Land‐Ocean Interface: A Case Study From the Amazon Shelf. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 23(11). Access the paper: 10.1029/2022gc010543
Spiegel, T., Vosteen, P., Wallmann, K., Paul, S.A.L., Gledhill, M. & Scholz, F. (2021). Updated estimates of sedimentary potassium sequestration and phosphorus release on the Amazon shelf. Chemical Geology (560). Access the paper: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2020.120017
