New neodymium data in the North East Atlantic Ocean allow progressing on the behaviour of this geochemical tracer
High-resolution vertical profiles of neodymium (Nd) concentrations and isotopic compositions were measured at the eastern part of the US GEOTRACES North Atlantic Zonal Transect (GA03, Gulf of Cadiz – Mauritanian Shelf – Cape Verde Islands). This allowed documenting impacts of different environmental settling on the tracer’s behaviours: the Mediterranean Outflow Waters (MOW), the Saharan dust plume, the Mauritanian margin with nepheloid layers and an Oxygen Minimum Zone (OMZ).
Distinguishing water masses in this oceanic area was a difficult task due to the relative uniformity of their Nd isotopic composition. Except in the Gulf of Cadiz, where MOW displays distinctively more radiogenic values than the surrounding waters (indicating the advection from the western North Atlantic Central Water from the West Atlantic).
Other striking features are: highest Nd concentrations below the Saharan dust plume with non radiogenic Nd; first documented release of mostly scavenged Nd within an OMZ; and, a prominent benthic nepheloid layer at the bottom of the Mauritanian margin, which favours the release of non radiogenic Nd. Thorough treatments of these data allow disentangling horizontal transports from biogeochemical processes in this area.
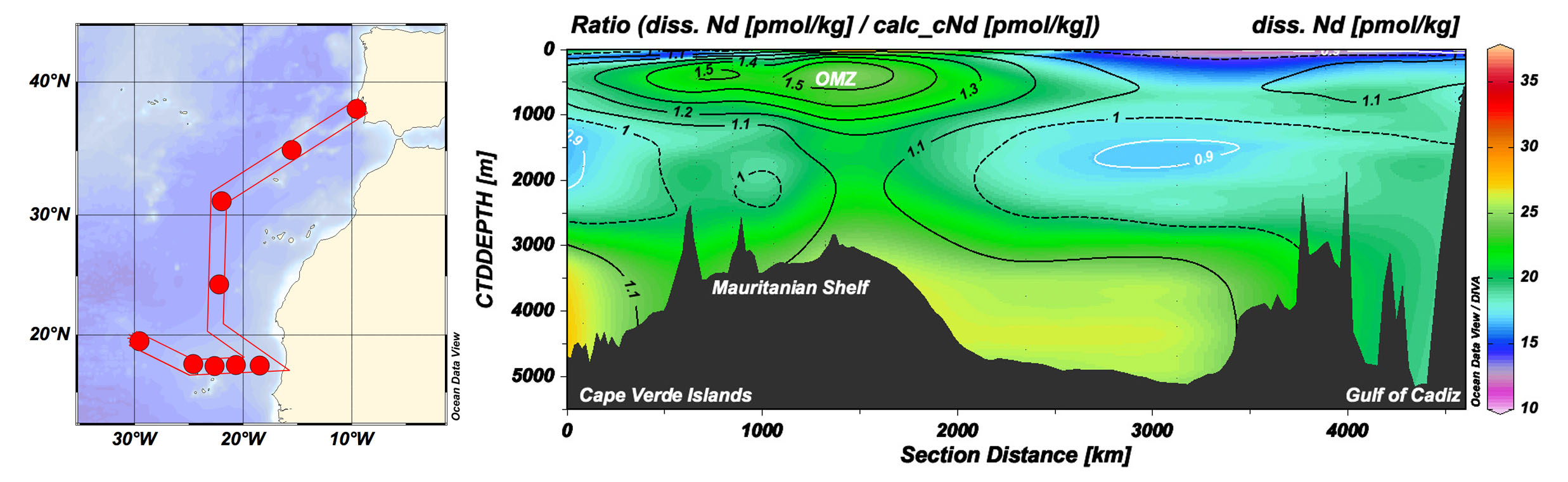
Figure: Map of the cruise track and stations with a section along GA03 (Cape Verde Islands – Mauritanian Shelf – Gulf of Cadiz, from left to right) showing measured Nd concentrations (colour shading) overlain by the ratio of expected to actual Nd concentrations (iso-lines). Values >1 indicate excess of Nd with respect to water mass mixing, which is particularly the case within the OMZ at ~500m between section distance 0 and ~2500km. Click here to view the figure larger.
Reference:
Stichel, T., Hartman, A. E., Duggan, B., Goldstein, S. L., Scher, H., & Pahnke, K. (2015). Separating biogeochemical cycling of neodymium from water mass mixing in the Eastern North Atlantic. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 412, 245–260. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2014.12.008 Click here to access the paper.
